Figure 2.
Granule-Permissive-Sized Clearances Persist following Degranulation and Are a Feature of NK and Cytotoxic T Cells
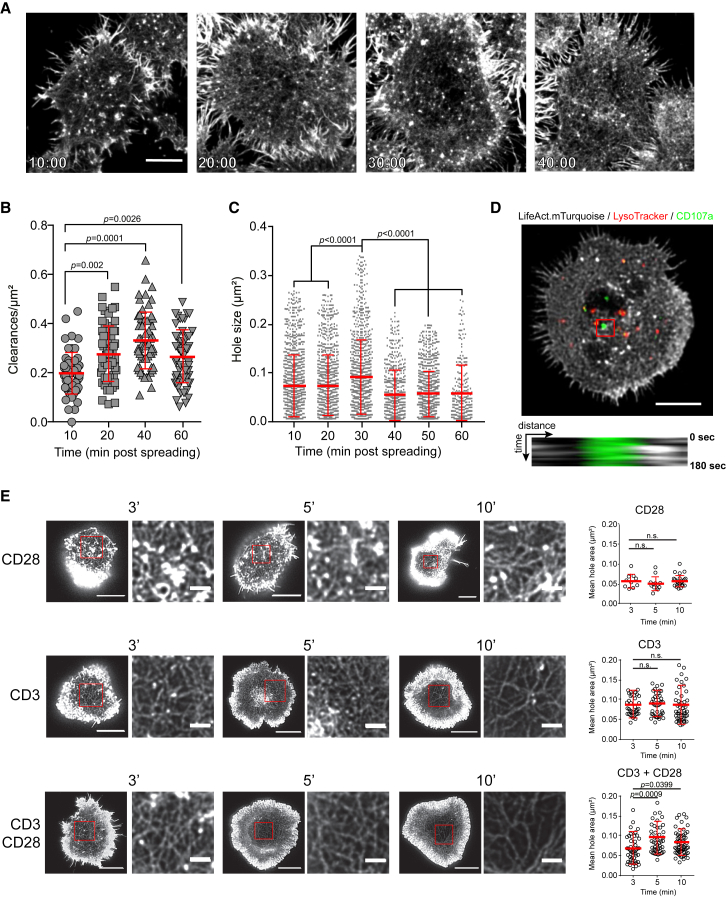
(A) Representative images of NK92 activated on anti-CD18- and anti-NKp30-coated glass for the times indicated, stained for F-actin, and imaged by time-gated STED microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(B) Quantification of the clearances/μm2 measured in activated NK92. Each data point represents one cell from N = 58, 59, 59, and 59 cells from 4 pooled independent repeats. The p value was calculated by ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparison.
(C) Quantification of mean hole area measured in fixed activated NK92 cells acquired by SIM at the indicated time points. N = 20 cells per condition; the experiment is representative of 3 independent repeats.
(D) Representative images of NK92.LifeAct-mTurquoise cells showing F-actin (gray), lytic granules (red), and CD107a (green). Scale bar, 5 μm. The kymograph (below) produced from the region highlighted by the red square shown for and showing F-actin (gray) and CD107a (green). Images are representative of 20 cells from 2 independent experiments.
(E) Primary human T cells were isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors and activated on anti-CD3, anti-CD28, or anti-CD3/-CD28 for the times indicated prior to fixation and staining with phalloidin Alexa Fluor 488. Cells were imaged by time-gated STED microscopy. The regions inside the red boxes are magnified on the right of each panel. Scale bars, 5 μm and 1 μm (insets). Mean hole area was measured and is shown in the graph (right) of each condition. N = 10, 13, 24, 37, 41, 50, 49, 50, and 61 cells, respectively, pooled from 3 independent repeats. The p value was calculated by one-way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis test (Dunn’s). Similar analysis was performed in primary T CD8+ and NK cells in Figure S2.