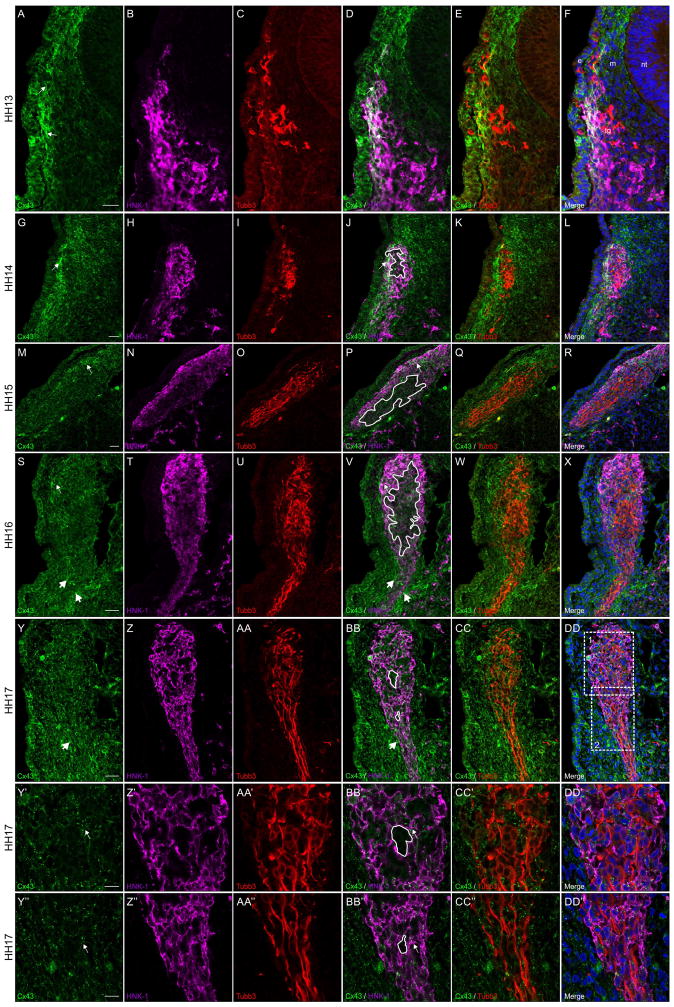
Figure 4. Connexin 43 is observed in neural crest cells but is absent in placodal neurons contributing to trigeminal ganglion.
Representative transverse sections taken through the forming trigeminal ganglion at HH13-HH17 followed by immunostaining for Connexin 43 (green), HNK-1 (purple), and Tubb3 (red). White boxes 1 and 2 in (DD) indicate Y-DD’ and Y’’-DD’’, respectively. Connexin 43 is noted in HNK-1-positive neural crest cells at the outer edge of the trigeminal ganglion adjacent to the surface ectoderm (A, D, G, J, M, P, S, and V, arrows) and at lower levels within the center of the trigeminal ganglion (J, P, V, BB, BB’, and BB’’, tracings), where the Tubb3-positive placodal neurons are located (C, E, I, K, O, Q, U, W,AA, CC, AA’, CC’, AA’’, and CC’’). At HH13, only the HNK-1-positive neural crest cells adjacent to the surface ectoderm are strongly Connexin 43-positive while those adjacent to the mesenchyme are less immunoreactive (A, B, D, and F). At HH14, Connexin 43 expression is reduced in the surface ectoderm but neural crest cells are still Connexin 43-positive (G, H, J, and L). At HH15 and HH16, on the other hand, there is increased mesenchymal expression of Connexin 43 along the distal projection of the ganglion (S, V, Y, and BB, large arrows). In HH17 embryos, at higher magnification, it is clear that placodal neurons do not express Connexin 43 (compare tracings in BB’ and BB’’ to Tubb3-positive placodal neurons in CC’ and CC’’). Scale bars in (A), (G), (M), (S), and (Y) are 20 μm and apply to (B–F), (H–L), (N–R), (T–X), and (Z-DD), respectively; scale bars in (Y’) and (Y’’) are 10 μm and apply to (Z’-DD’) and (Z’’-DD’’), respectively. Ectoderm is indicated by an (e), neural tube by an (an), mesenchyme by an (m), and the trigeminal ganglion by (tg) in (F) for orientation.