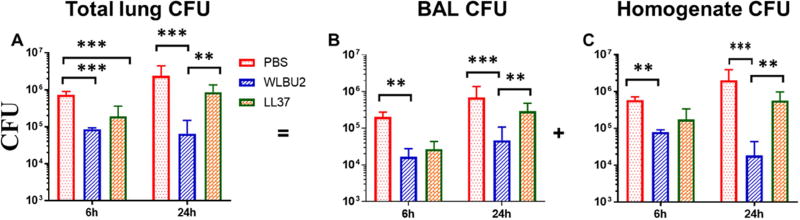
Figure 2. WLBU2-treated mice are protected against PAO1-induced respiratory infection.
Age- and gender-matched wild-type C57BL/6J mice were intra-tracheally (i.t.) instilled with 3×106 CFU PAO1 per mouse. Total lung burden (A) was represented by combining bacterial CFU in BAL (B) and lung homogenate (C) after necropsies at 6h and 24h after PAO1 infection. WLBU2-treated mice showed a significant reduction in their lung bacterial burden compared to LL37- and mock-treated mice. Results are mean ± SEM from two independent experiments; n = 4–6 mice for each treatment group in each experiment; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.