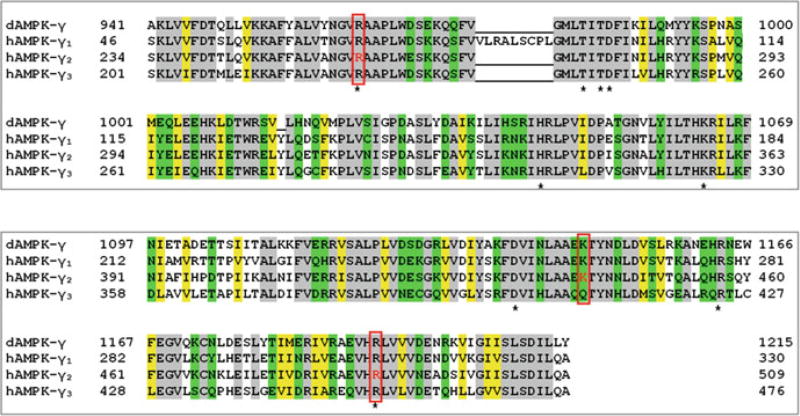
Fig. 16.2. Alignment of human and Drosophila AMPK-γ.
CBS domains of AMPK are highly conserved between H. sapiens and D. melanogaster. Most amino acids in the CBS domains of Drosophila AMPK-γ (NP_732598.1) and human AMPK-γ1–3 (γ1, NP_001193638.1; γ2, NP_001035723.1; γ3, NP_059127.2) are either invariant (gray) or have residues with conserved hydrophilicity (green) or hydrophobicity (yellow). In SNF4 (dAMPK-γ), the first pair of CBS domains spans from amino acids 941–1069, while the second pair spans from amino acids 1097–1215 (Marchler-Bauer et al. 2015). Human AMPK-γ2 amino acids highlighted in red represent conserved residues that, when mutated, can lead to cardiomyopathy in humans (Burwinkel et al. 2005; Liu et al. 2013; Moffat and Harper 2010). Stars indicate some of the conserved amino acid residues that have been shown to mediate nucleotide binding at regulatory sites in crystal structures containing a specific transcript variant of rat AMPK-γ1 (Chen et al. 2012; Xiao et al. 2007). Note: Amino acid numbering will vary among transcript variants; the numbering listed in the figure corresponds to the provided accession numbers