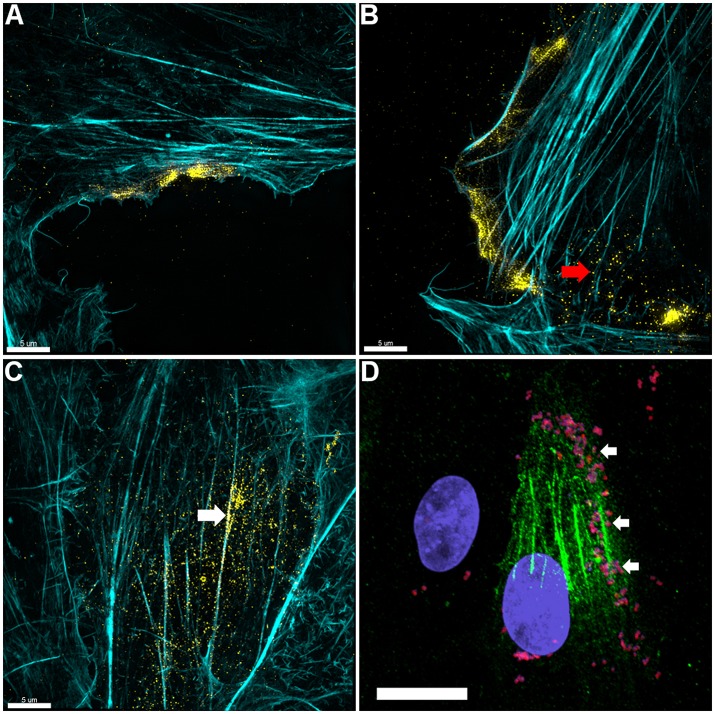
Figure 3.
Actin is expressed on the surface of PK-15 cell monolayers. (A–C) Localization of actin on the surface of PK-15 cells. Uninfected monolayers were grown to semi-confluency, fixed in methanol-free paraformaldehyde, incubated with mAbβ−act prior to permeabilization, and conjugated to anti-murine CF™ 488 (yellow). F-actin was then stained using phalloidin (cyan) after permeabilization. Surface exposed actin can be seen accumulating at the leading edge (A,B) of cells in the monolayer as well as on the surface of cells along filaments that stained intensely with phalloidin (C). Red arrow in (B) indicates what appears to be globular extracellular actin while the white arrow in (C) demonstrates extracellular actin that appears to colocalize with F-actin. (D) M. hyopneumoniae cells adhere on the surface of PK-15 cells in regions enriched with surface actin. M. hyopneumoniae cells (magenta colored cells indicated by white arrows) were labeled with F2P94−J antisera conjugated to CF™ 568 (red) and in this case, surface actin appears green. The nuclei of M. hyopneumoniae and PK-15 cells were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars in (A–C) are 5 and 20 μm in (D).