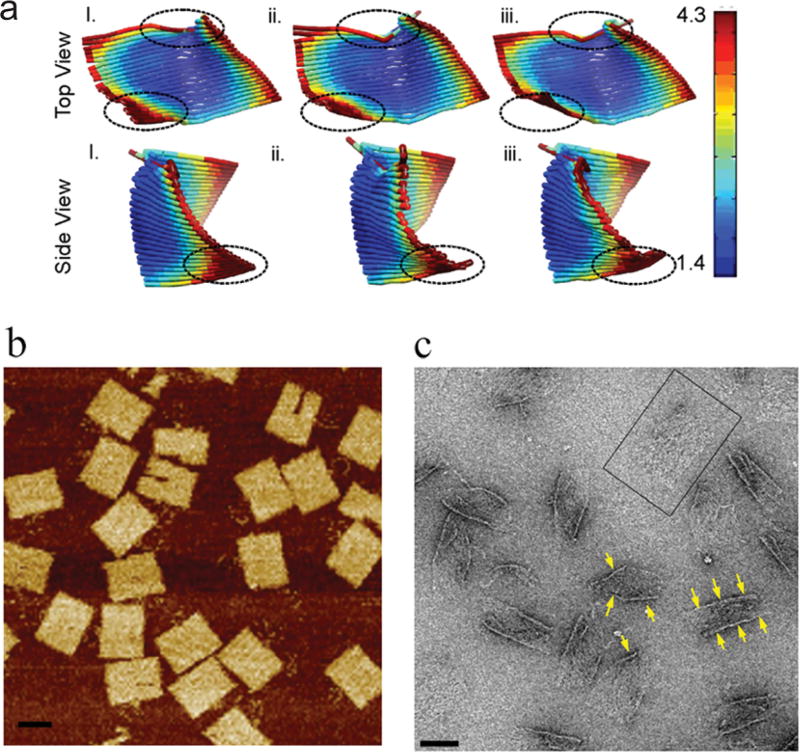
Figure 1.
Flexibility of 2D DNA origami rectangles as observed by computational modeling, AFM and EM. (a) Flexibility prediction of DNA tiles using computer-aided engineering for DNA origami (CanDo) software available online (http://cando-dna-origami.org/).25 Snapshots from CanDo-generated movies that show extreme curling of the origami edges. The top panel depicts the top view, whereas the bottom panel depicts the side view. The dotted circles indicate particularly flexible regions. The heat map scale indicates the level of flexibility. (b) Representative AFM images of the DNA origami used in this study. The scale bar is 50 nm. (c) Negative stain EM image showing flexibility and variable folding (highlighted by arrows) of 2D origami. Flat DNA origami tiles (such as the one boxed) were rarely observed. The scale bar is 50 nm.