FIGURE 2.
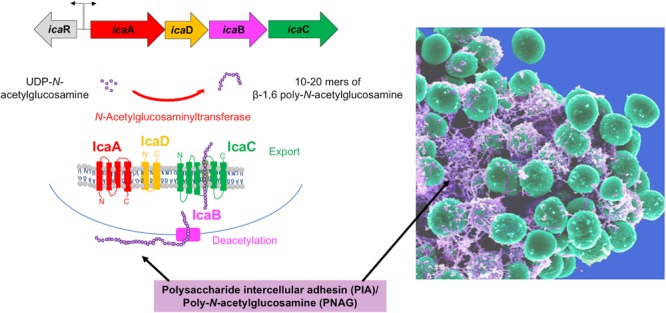
The biofilm exopolysaccharide PIA/PNAG. The PIA biosynthetic locus includes the icaA gene, which codes for an N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) transferase, which adds GlcNAc residues to a growing poly-GlcNAc chain. IcaD assists in this function in an unknown way. The chain is then believed to be exported by IcaC, because in the absence of icaC, polymerization stops at chain lengths of about 10–20 GlcNAc units. IcaB is located at the extracellular cell surface and de-acetylates some of the GlcNAc units, introducing a positive charge in the polymer due to the then unmasked amino groups. This is necessary for PIA surface location (see electron microscopy picture on the right) and functionality in biofilm formation and immune evasion.
