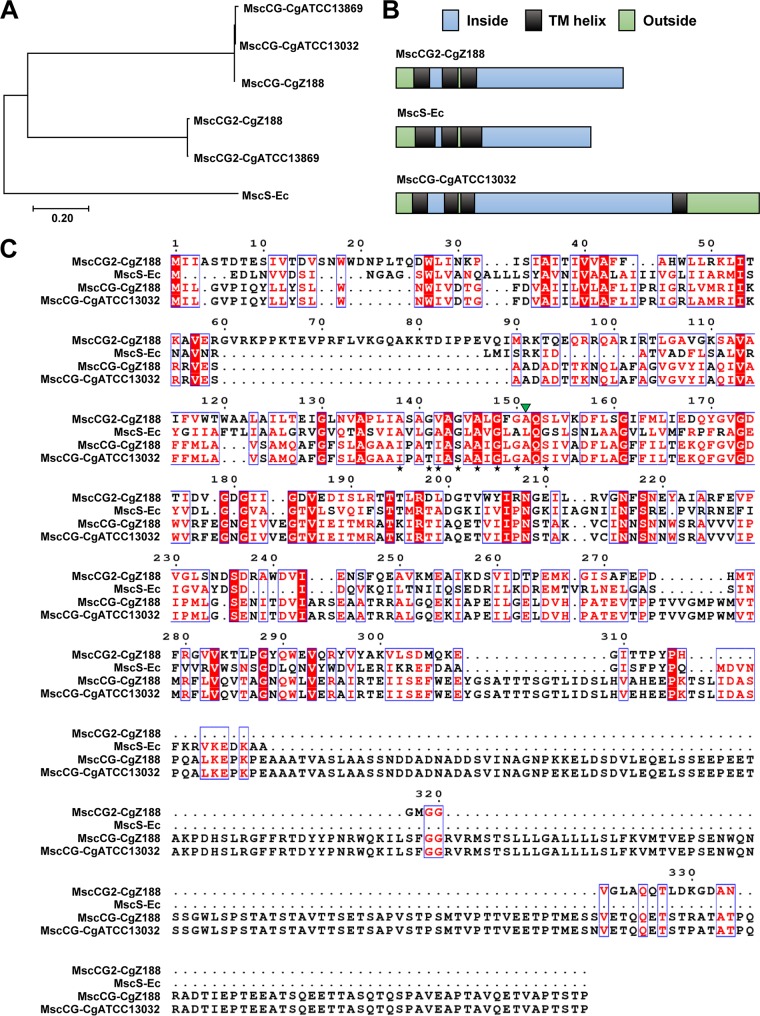
FIG 2.
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of amino acid sequences of MscS-like proteins. The tree was constructed with the MEGA 7 program using the neighbor-joining method (29). CgATCC13869, CgATCC13032, and CgZ188 represent C. glutamicum strains ATCC 13869, ATCC 13032, and Z188, respectively. Ec, E. coli. (B) Membrane topology of MscS-like proteins. Membrane topology of MscCG2 from C. glutamicum Z188 was predicted by TMHMM Server v.2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM) (38). Membrane topologies of MscS from E. coli and MscCG from C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 were proposed based on previous studies (10, 12, 14). (C) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of MscS-like proteins (numbering relative to MscCG2 from C. glutamicum Z188). The alignment was conducted with the ESPript 3 program (http://espript.ibcp.fr) (39). Black stars represent the conserved l-alanine and glycine present in the third TM helix of E. coli MscS. The green triangle represents the residue involved in a gain-of-function mutation in gating of MscCG (20).