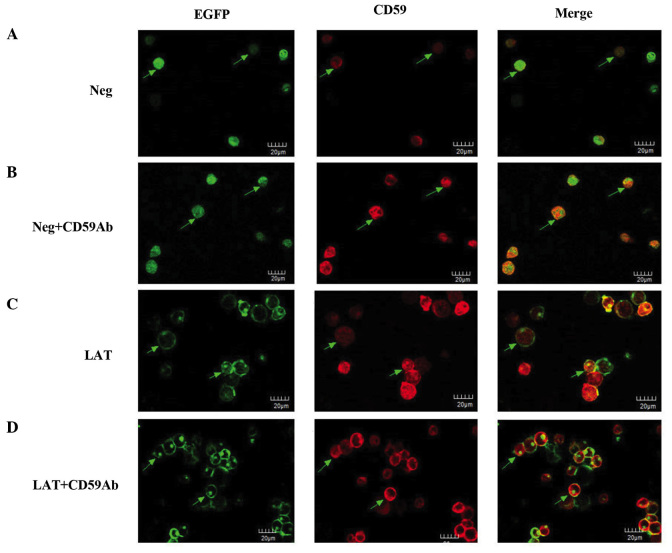
Figure 2.
Cellular localization of CD59 and LAT. (A) Neg group. Jurkat cells transfected with neg-EGFP lentiviruses showed green fluorescence corresponding to EGFP in the cytoplasm. CD59 molecules were stained red on the cytomembrane of the neg group cells. The merged images showed green and red fluorescence in neg cells corresponding to EGFP and CD59, respectively. (B) Neg + CD59Ab group. Neg cells were stimulated with CD59Ab. Green fluorescence corresponding to EGFP was expressed in the cytoplasm. CD59 red fluorescence was higher following stimulation with CD59Ab, as compared with the neg group. The merged images showed green and red fluorescence corresponding to EGFP and CD59, respectively, in neg cells following CD59Ab stimulation. (C) LAT group. Jurkat cells transfected with LAT-EGFP lentiviruses showed green fluorescence corresponding to LAT on the cell surface. CD59 was stained red on the cytomembrane of LAT group cells. The merged images showed colocalization of LAT and CD59 molecules to lipid rafts. (D) LAT + CD59Ab group. LAT group cells were stimulated with CD59Ab. Green fluorescence on the cell surface corresponding to LAT was higher in the LAT + CD59Ab group cells compared with the LAT group cells. Similarly, CD59 staining was higher in the LAT + CD59Ab group cells compared with the LAT group cells. The merged images showed that LAT and CD59 molecules were colocalized to lipid rafts in LAT cells stimulated with CD59Ab. CD59Ab, cluster of differentiation 59 antibody; LAT, linker for activation of T-cells; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein.