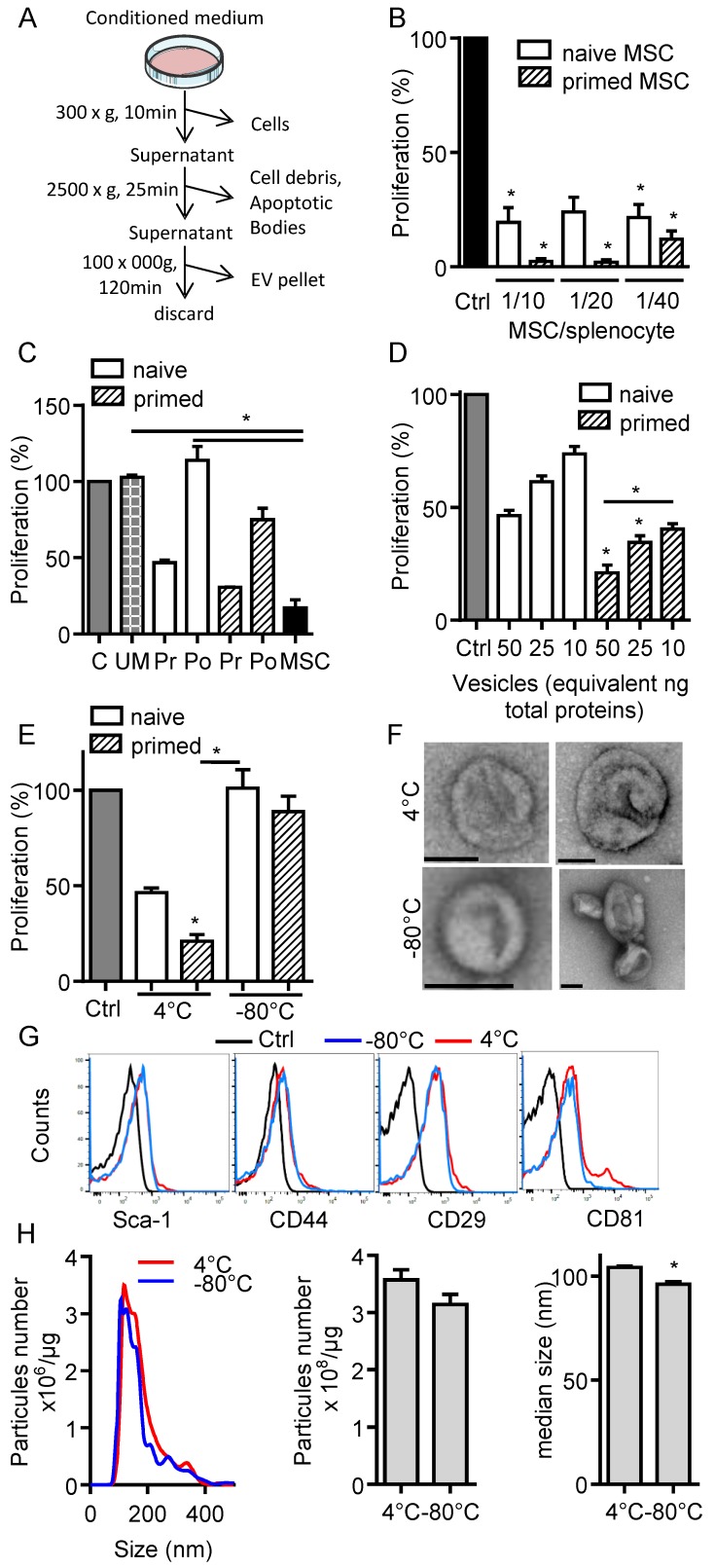
Figure 1.
Freshly isolated extracellular vesicles from murine MSCs exert immunosuppressive functions. (A) Experimental protocol for isolation of total extracellular vesicles (EVs) using differential ultracentrifugation. (B) Proliferation of Concanavalin A-activated murine splenocytes cultured alone for 3 days (Ctrl) or incubated with naïve or IFN-γ (20 ng/mL)-primed MSCs (n=3 biological replicates). (C) Proliferation of Concanavalin A-activated murine splenocytes cultured alone for 3 days (C) or incubated with ultracentrifuged production medium (UM) or naïve MSCs or MSCs-conditioned medium (CM) pre (Pr)- or post (Po)-100,000 × g centrifugation according to (A). CM was depleted in cells and debris (by 300 × g and 2500 × g centrifugation steps). MSCs were naïve or primed with 20 ng/mL IFN-γ (n=3 biological replicates). (D) Proliferation of Concanavalin A-activated murine splenocytes cultured alone for 3 days (Ctrl) or incubated with increasing amounts of EVs (n=4 biological replicates). (E) Proliferation of Concanavalin A-activated murine splenocytes cultured alone for 3 days (Ctrl) or incubated with 50 ng of freshly isolated or freeze-thawed EVs (n=4 biological replicates). (F) TEM analysis of freshly isolated (4°C) or freeze-thawed EVs (-80°C). Bar is 100 nm. (G) Expression of MSCs membrane markers (Sca-1, CD44, CD29) and of CD81 exosomal marker on freshly isolated (4°C) or freeze-thawed EVs (-80°C) analyzed by flow cytometry. (H) Number and median size of freshly isolated (4°C) or freeze-thawed EVs (-80°C) by Nano Tracking Analysis. Statistical analysis used a non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison post-test (B, C, D, E) or a Mann-Whitney test (H). *: p<0.05.