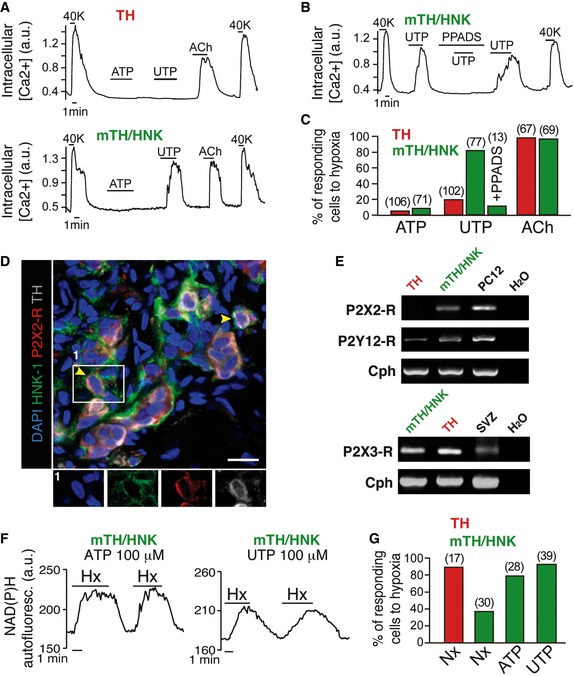
Intracellular calcium concentration measurements in mature glomus cells (TH) and neuroblasts (mTH/HNK) in response to purinergic (ATP and UTP) and cholinergic (acetylcholine, Ach) agonists. 40K = 40 mM extracellular potassium chloride.
Intracellular calcium concentration recording from a CB neuroblast (mTH/HNK), showing inhibition of the response to UTP by the purinergic receptor blocker PPADS. 40K = 40 mM extracellular potassium chloride.
Quantification of cells responding to different purinergic and cholinergic agonists (number of total cells studied is indicated between brackets). Note how CB neuroblasts respond better to the more potent purinergic agonist UTP.
Histological immunodetection of purinergic receptor P2X2 expression in CB neuroblasts (mTH+/HNK‐1+). Scale bar: 25 μm.
RT–PCR detection of expression of different ionotropic and metabotropic purinergic receptors in both mature glomus cells (TH) and neuroblasts (mTH/HNK).
Increases in mitochondrial NAD(P)H in response to hypoxia in CB neuroblasts incubated with ATP or UTP for 24–48 h, demonstrating maturation induced by purinergic signaling.
Quantification of hypoxia‐responsive cells, as measured by NAD(P)H levels, after incubation for 24–48 h in the indicated conditions (number of total cells studied is indicated between brackets).
Data information: Data in bar graphs are presented as the sum of responding cells among total cells studied. Cells used for the analysis in panels (A–C), (F), and (G) were obtained in eight independent experiments with four rats each.