Figure 8.
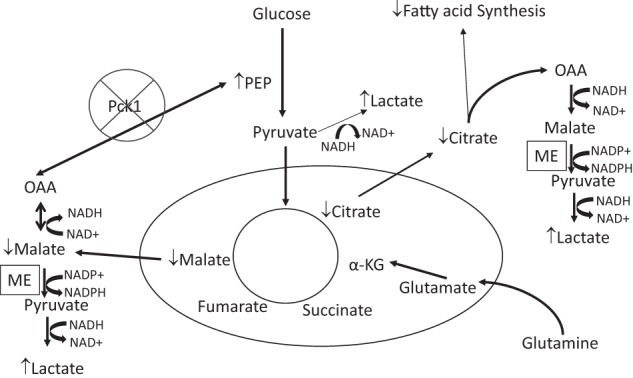
Deletion of Pck1 in macrophage cells. The deletion of Pck1 results in increased lactate concentrations in the cell. The flux through pyruvate dihydrogen complex is reduced resulting in decreased citrate levels and reduced fatty acid synthesis. The deletion of Pck1 prevents the decarboxylation of OAA to PEP. Thus, OAA would be reduced by NADH to form malate; malate would be decarboxylated and oxidized to form pyruvate by the malic enzyme. This produces NADPH, which is used to generate ROS by NADPH oxidase. Generation of ROS serves as defense against invading microbes and is viewed as the assurance of monocyte/macrophage activation to M1-like phenotype.
