Figure 10.
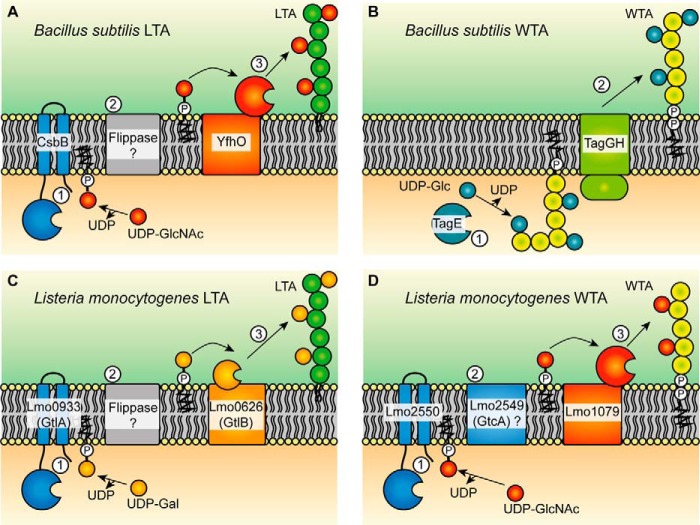
Models for the LTA and WTA glycosylation processes in B. subtilis and L. monocytogenes. A and B, proposed model for the glycosylation process of LTA (A) and WTA (B) in B. subtilis. A, based on the genetic data presented in this study, we suggest that LTA in B. subtilis is glycosylated with the aid of the cytoplasmic GT CsbB, which we predict transfers GlcNAc residues to the C55-P lipid carrier (step 1). The C55-P-GlcNAc intermediate is then transported across the membrane by an unknown flippase enzyme (step 2). We further hypothesize that the GlcNAc residues are then transferred onto LTA by the GT candidate enzyme YfhO (step 3). B, WTA of B. subtilis is modified with glucose residues in a process that takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and that is catalyzed as previously reported by the GT TagE, which uses UDP-glucose as substrate (step 1) (58). The glycosylated WTA is subsequently transported across the membrane via TagGH (step 2) (57). C and D, proposed model for the LTA (C) and WTA (D) glycosylation process in L. monocytogenes. C, LTA in L. monocytogenes is modified with galactose residues. In the first step, GtlA, which is thought to act as cytoplasmic GT, transfers galactose molecules onto the C55-P lipid carrier (29). The sugar-lipid intermediate is then transported across the membrane by an unknown flippase enzyme (step 2), and the galactose residues are subsequently transferred onto LTA on the outside of the cell, and we suggest that this step is catalyzed by GtlB (step 3). D, for WTA glycosylation in L. monocytogenes, the cytoplasmic GT Lmo2550 probably produces a C55-P-GlcNAc lipid intermediate (step 1) that is subsequently transported across the membrane by a flippase, a function that might be provided by Lmo2549 (also referred to as GtcA) (step 2). As final step, we suggest that Lmo1079, a B. subtilis YfhO homolog, transfers the GlcNAc molecule onto WTA on the outside of the cell (step 3).