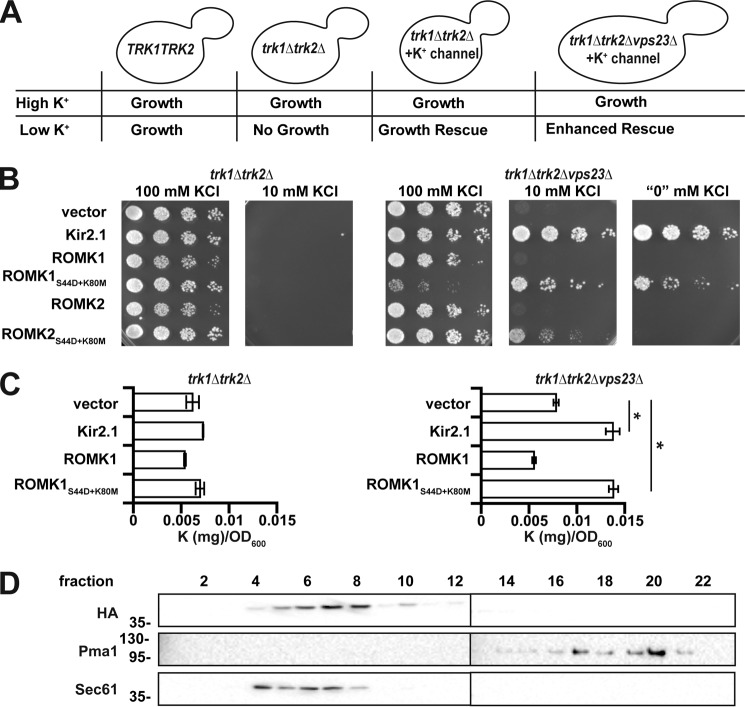
Figure 1.
ROMK1S44D+K80M rescues growth of trk1Δtrk2Δ yeast on low potassium and increases potassium uptake. A, representation of a yeast-based assay for potassium channel function. B, yeast strains with the indicated genotypes transformed with an empty expression vector control or vectors engineered to express Kir2.1, wildtype ROMK1, ROMK1S44D+K80M, ROMK2, or ROMK2S44D+K80M were serially diluted onto medium supplemented with the indicated amounts of KCl. C, intracellular potassium levels, as measured by ICP-MS, were assessed using equivalent amounts of yeast containing an empty vector or expressing Kir2.1, wildtype ROMK1, or ROMK1S44D+K80M. Cells were cultured for 8 h in liquid media containing either 100 or 10 mm KCl. Data show the means of three biological replicates. Error bars show standard deviations, *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test). D, Western blottings of sucrose gradient fractions showing migration of HA-tagged ROMK1S44D+K80M containing microsomes in wildtype yeast. Pma1 marks the plasma membrane-derived fractions, and Sec61 marks ER-derived fractions.