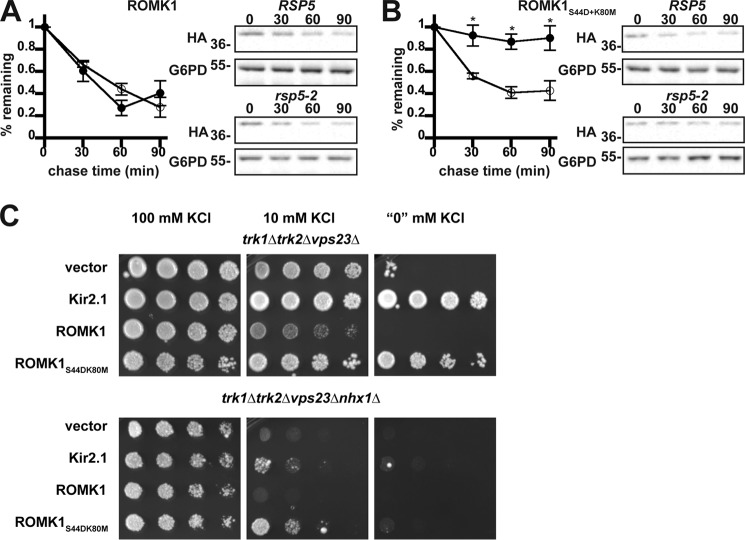
Figure 6.
Rsp5 promotes the degradation of ROMK1S44D+K80M and Nhx1 promotes recycling of ROMK. Yeast cultures expressing HA-tagged versions of either ROMK1 (A) or ROMK1S44D+K80M (B) grown to mid-logarithmic phase were dosed with cycloheximide, and aliquots were withdrawn at 0, 30, 60, and 90 min. Yeast strains containing a temperature-sensitive mutation in the gene encoding Rsp5 (rsp5-2, filled circles) or wildtype yeast (RSP5, open circles) expressing ROMK were shifted from room temperature to 39 °C 75 min before addition of cycloheximide. ROMK expression was assessed by Western blotting and normalized to the initial time point. Representative blots are shown, and all blots were stripped and reprobed for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) as a loading control. Data represent the means of four independent experiments. Error bars show standard errors of the mean, and * indicates a significant (p < 0.05) difference as assessed by Student's t test. C, yeast strains with the indicated genotypes transformed with an empty expression vector control or vectors engineered to express Kir2.1, wildtype ROMK1, or ROMK1S44D+K80M were serially diluted onto medium supplemented with the indicated amounts of KCl. All experiments were performed in duplicate, and a representative assay is shown.