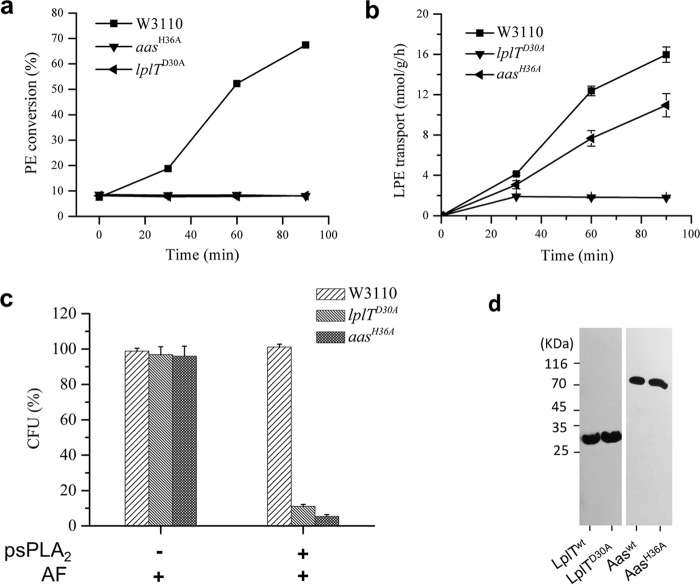
Figure 3.
E. coli resistance is determined by the function of LplT and Aas. a, LPE acylation assay of E. coli W3110, lplTD30A, and aasH36A strains. The activities were calculated based on conversion (%) of LPE to PE shown on TLC images in Fig. S2. b, LPE transport assays using spheroplasts generated from E. coli W3110 WT, lplTD30A, and aasH36A cells. The transport activity of LplT in each sample was calculated based on the acquired radioactivity in the spheroplasts. c, viability tests of E. coli W3110 WT, lplTD30A, and aasH36A strains (+ 12 units of psPLA2, ± 20 μl AF) for 90 min. The data are expressed as CFU (%) compared with untreated WT control. d, Western blotting analysis using anti-His antibody to examine LplTWT, LplTD30A, AasWT, or AasH36A protein expressed in E. coli. Cell lysates containing the same amount of total protein were loaded for each sample.