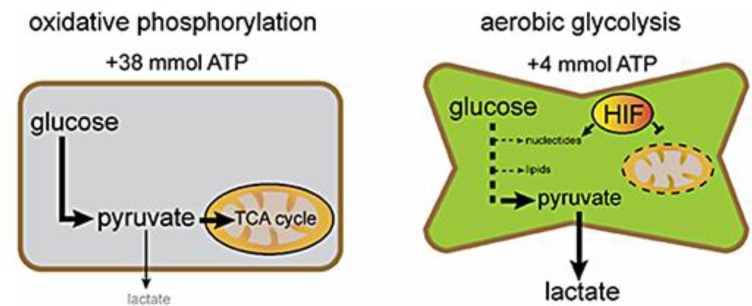
Fig. 1.
The differences in glucose metabolism between normal and cancerous tissues are shown. Oxidative phosphorylation in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, which yields large quantities of ATP, is the dominant metabolic pathway in differentiated cells. Cancer cells, in contrast, preferentially use glycolysis, which is assumed to be driven by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) and yields numerous precursors of cell constituents, but limited amounts of ATP.