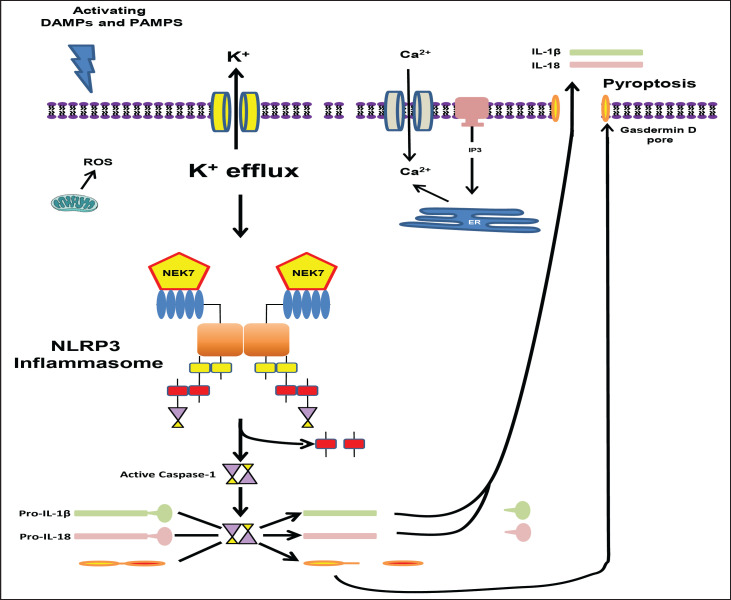
Fig. 3.
Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the canonical pathway. The second step of the canonical pathway is activation. DAMPs and PAMPs trigger this step and lead to activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Proposed cellular events involved include ROS, Ca2+ signaling, and, most likely, K+ efflux. Regardless, NLRP3 inflammasome assembly is initiated and the catalytic domain of the never in mitosis gene a-related kinase 7 interacts with the LRR domain of NLRP3 causing oligomerization through binding of NACHT domains (the figure depicts only a dimer for simplicity). This leads to NLRP3 binding to ASC and ASC in turn binding to pro-caspase-1. Pro-caspase-1 molecules in close proximity lead autocatalytic cleavage of pro-caspase-1 to caspase-1 (induced proximity). Activated caspase-1 then cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their active forms (IL-1β and IL-18). Caspase-1 also cleaves gasdermin D whose N-terminus is responsible for forming a pore that results in pyroptosis and the release of IL-1β and IL-18.