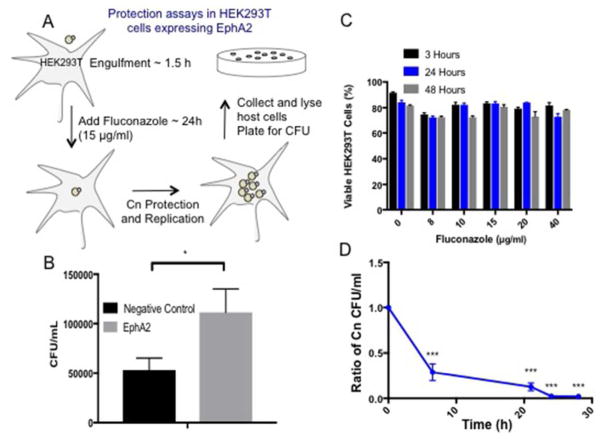
Fig 9. EphA2 is responsible for the internalization of C. neoformans in HEK293T that overexpress EphA2.
(A) To establish whether EphA2 acted directly to internalize C. neoformans a cell protection assay was performed. HEK293T cells overexpressing EphA2 were exposed to C. neoformans for 1.5h, subsequently washed away and replaced with fluconazole (15μg/ml), a static antifungal drug. Following a further 48h co-incubation where internalized C. neoformans was protected from fluconazole and allowed to replicate, HEK293T cells were lysed and plated for CFU determination (B) Significantly more CFUs from HEK293T overexpressing EphA2 than HEK293T cells alone (transformed with an empty plasmid) were detected, suggesting that EphA2 was directly responsible for the internalization of C. neoformans. (C & D) Prior to the assay, fluconazole activity was monitored to ensure HEK293T cells remained viable and fungal cells were susceptible.