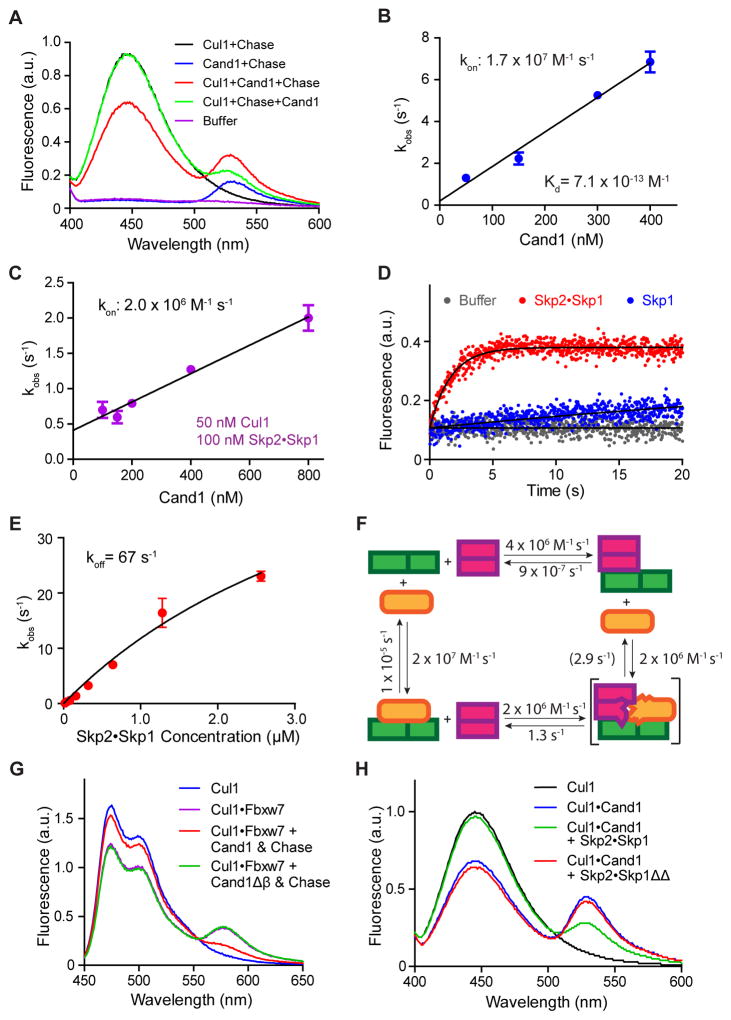
Figure 1. Properties of interactions among Cul1, Cand1 and Skp1•F-box protein revealed by FRET.
(A) FRET assay for Cand1•Cul1 complex formation. Fluorescence emission spectra from excitation at 350 nm of 70 nM Cul1AMC•Rbx1, 70 nM FlAsHΔH1Cand1, a mixture of the two (FRET), chase control for FRET, or buffer alone. +Chase indicates 700 nM Cand1. Proteins were added in the indicated order. Addition of chase to Cul1+Cand1 had a negligible effect on FRET due to the long t1/2 of the Cand1•Cul1 complex as shown previously (Pierce et al., 2013).
(B) kon for Cand1 binding to Cul1. The observed rates of Cand1•Cul1 assembly at different concentrations of Cand1 are plotted. Linear slope gives kon of 1.7 × 107 M−1s−1. Error bars, ± SEM, n = 5 (see also Fig S1A).
(C) kon for Cand1 binding to Cul1•Rbx1 preassembled with FBP. Similar to Fig 1B, except with 100 nM Skp1•Skp2 preincubated with 50 nM Cul1AMC•Rbx1. Linear slope gives kon of 2.0 × 106 M−1s−1. Error bars, ± SEM, n ≥ 4 (see also Fig S1B).
(D) Disruption of Cand1•Cul1 by Skp1•Skp2. The change in donor fluorescence versus time was measured following addition of 75 nM Skp1•Skp2 or 75 nM Skp1 to 25 nM FlAsHΔH1Cand1•Cul1AMC•Rbx1.
(E) koff of Cand1 from ternary exchange intermediate. The single exponential observed rates of Cand1 dissociation from 10 nM FlAsHΔH1Cand1•Cul1AMC•Rbx1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of Skp1•Skp2 were measured (see Fig S1C) and plotted. Fitting of the curve predicts a rate plateau at 67 sec−1. Error bars, ± SEM, n ≥ 3.
(F) Kinetic model of the exchange cycle. The number in parentheses indicates the koff of 2.9 s−1 calculated from detailed balance relations (see Fig S4C).
(G) Deletion of β hairpin in Cand1 enables formation of a stable complex comprising Cul1, Skp1•Fbxw7, and Cand1. Cand1 or Cand1Δβ (100 nM) was added to 70 nM CFPCul1•Rbx1•Skp1•Fbxw7TAMRA, and formation of SCFFbxw7 was monitored by FRET. + Chase indicates 700 nM Skp1•Skp2.
(H) Deletion of loop regions in Skp1 enables formation of a stable complex comprising Cul1, Skp1•Skp2, and Cand1. Skp1•Skp2 or Skp1ΔΔ•Skp2 (700 nM) was added to 70 nM FlAsHCand1•Cul1AMC•Rbx1 and the persistence of the latter complex was monitored by FRET.