Figure 5.
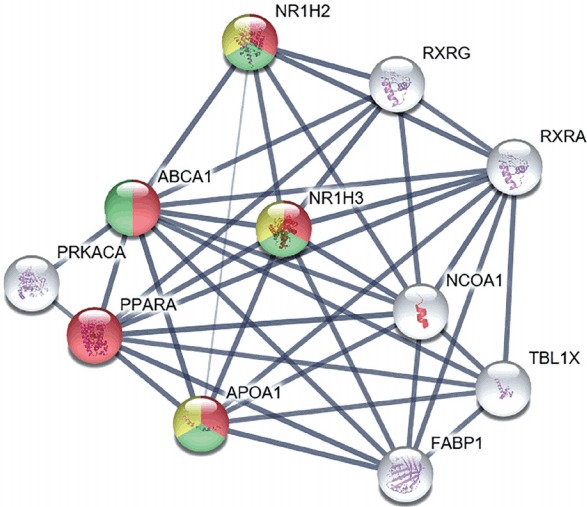
Bioinformatic analysis of ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1), revealing its preventive role in carotid plaque rupture and atherosclerosis progression during the inflammatory reaction. Bioinformatic analysis demonstrated that ABCA1 is involved in the regulation of lipid transport and in further inflammatory reactions involved in atherosclerosis progression. The thickness of strings describes the strength of data confidence. Among the primary interactions of ABCA1, 10 proteins with the highest confidence scores are shown in the figure. The biological processes of ABCA1 are distinguished by different colors: regulation of lipid transport in red, regulation of cholesterol transport and homeostasis in green, and negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway and immune response in yellow. The remaining proteins that interact with ABCA1 are depicted by white color. NR1H2, nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 2; RXRG, retinoid X receptor gamma; RXRA, retinoid X receptor alpha; NR1H3, nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group H member 3; PRKACA, protein kinase A catalytic subunit alpha; PPARA, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; NCOA1, nuclear receptor coactivator 1; APOA1, apolipoprotein A1; TBL1X, transducin beta like 1 X-linked; FABP1, fatty acid binding protein 1.
