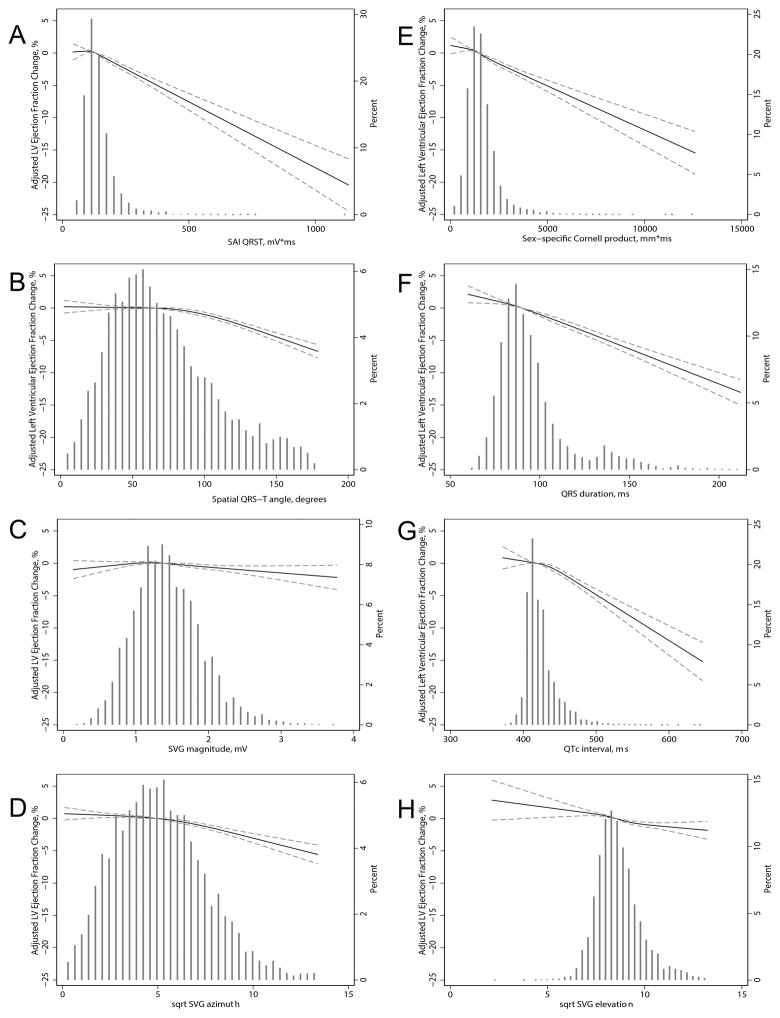
Figure 3. Cross-sectional analysis.
Fully adjusted (by age, sex, race, CHD, HF, hypertension, diabetes, BMI, smoking, presence of ventricular conduction abnormalities, heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure) association between (A) SAI QRST, (B) spatial QRS-T angle, (C) SVG magnitude, (D) sqrt-SVG azimuth, (E) Cornell product, (F) QRS duration, (G) QTc interval, (H) sqrt-SVG elevation and LV ejection fraction. The models adjusted for age, sex, race, BMI, CHD, HF, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, and blood pressure. Restricted cubic spline with 95% confidence interval shows change in LVEF (Y-axis) in response to ECG predictor (X-axis); 50th percentile of predictor variable is selected as the reference.