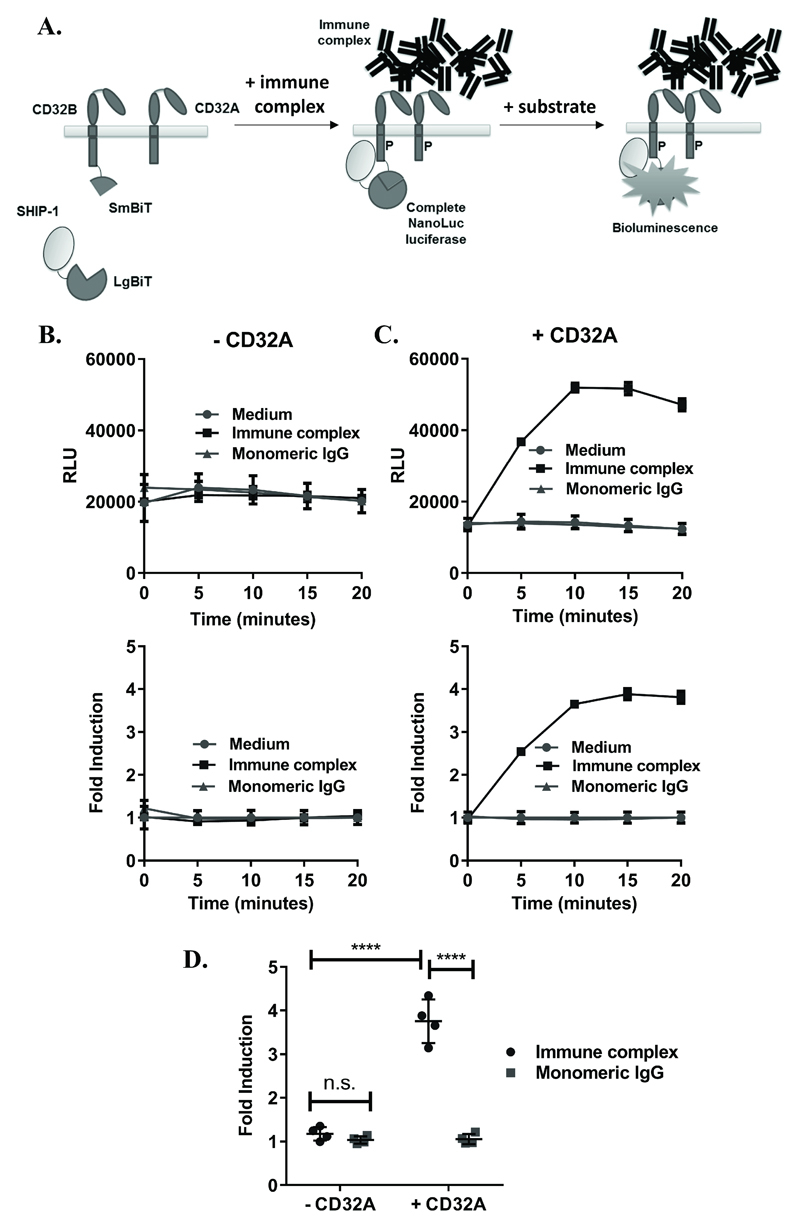
Figure 1. Development of an assay for detection of IC-mediated SHIP-1 recruitment.
(A) Assay concept: (Left) cells expressing CD32B and SHIP-1 with complementary SmBiT and LgBiT fusions, respectively, and CD32A with no fusion. (Middle) Following stimulation with IC, SHIP-1 is recruited to the phosphorylated (P) ITIM of CD32B, leading to interactions between LgBiT and SmBiT fragments to form complete NanoLuc enzymes. (Right) In the presence of a NanoLuc substrate, complete luciferase enzymes produce luminescence, reflecting SHIP-1 recruitment to CD32B. NB: Monomeric IgG, being unable to crosslink FcγRs, is not expected to induce SHIP-1 recruitment, resulting in no increase in luminescence. (B-C) HEK293F cells, transiently co-transfected with CD32B-SmBiT and SHIP-1-LgBiT (C-terminus) alone (B) or with CD32A (C) on d0, were stimulated with medium, IC or monomeric IgG (10µg/ml) on d1. Luminescence readings were taken at time 0 following substrate addition, and at 5 minute intervals following stimulation. Responses are shown as (top) relative luminescence units (RLU) or (bottom) fold inductions of response relative to medium control (fold induction). Means ± S.D. of technical replicates are shown. (D) Mean fold inductions (at 15 minutes) from repeat experiments where cells were co-transfected as in (C) and treated with monomeric IgG or IC on d1, as above (n=4 experiments). Statistical significance between groups was assessed using a 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. **** – p<0.0001; n.s. – not-significant.