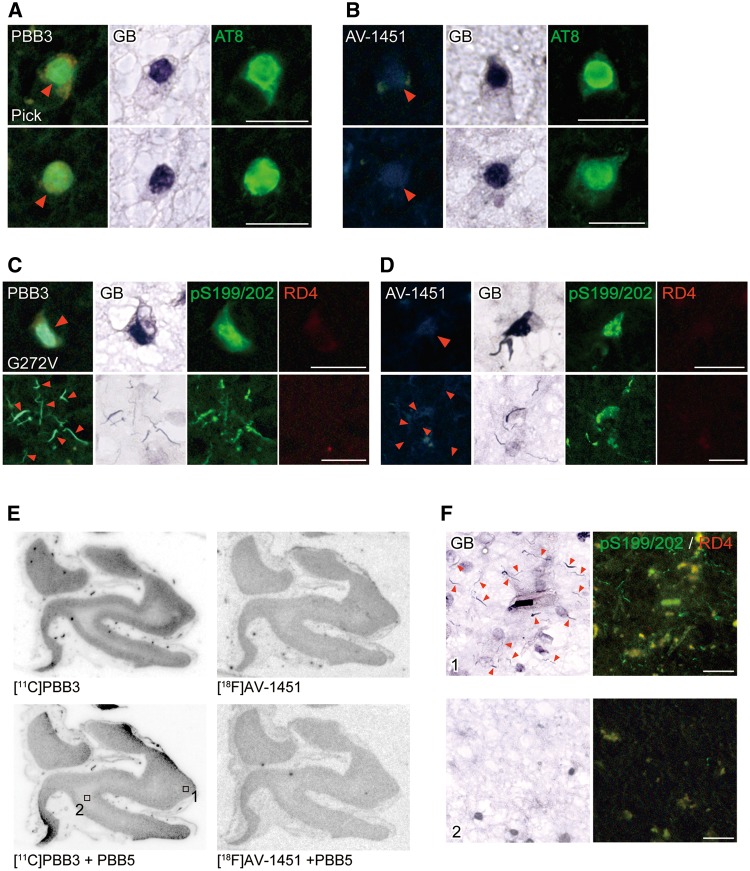
Figure 6.
Binding of non-labelled and radiolabelled PBB3 and AV-1451 to tau lesions in the frontal cortex of patients with Pick’s disease and FTDP-17 due to the G272V MAPT mutation. (A and B) Staining of Pick bodies in the frontal cortex of a Pick’s disease patient with 56.5 µM of PBB3, AT8 and GB (A), and with 56.5 µM of AV-1451, AT8 and GB (B). (C and D) Quadruple staining of tau lesions in the frontal cortex of an FTDP-17 patient due to the G272V MAPT mutation with 56.5 µM of PBB3, pS199/pS202, RD4 and GB (C), and with 56.5 µM of AV-1451, pS199/pS202, RD4 and GB (D). (E) Autoradiographic labelling of closely adjacent sections of the frontal cortex derived from an FTDP-17 patient due to the G272V MAPT mutation with 10 nM of 11C-PBB3 (left) and 18F-AV-1451 (right) in the absence (top) and presence (bottom) of 100 µM of non-radioactive PBB5. (F) High-power photomicrographs of triple staining with GB, pS199/pS202 and RD4 in areas indicated by squares in E. Intense GB staining was abundantly observed in grey matter (area 1), consistent with the pattern of autoradiographic signals of 11C-PBB3 in E. These strongly GB-positive inclusions were almost absent in white matter (areas 2), as reflected by minimal autoradiographic labelling with 11C-PBB3 in E. Arrowheads in A and B indicate Pick bodies and those in C, D and F indicate tau inclusions comprised of 3-repeat isoforms. Scale bars = 20 µm (A–D and F).