Figure 3.
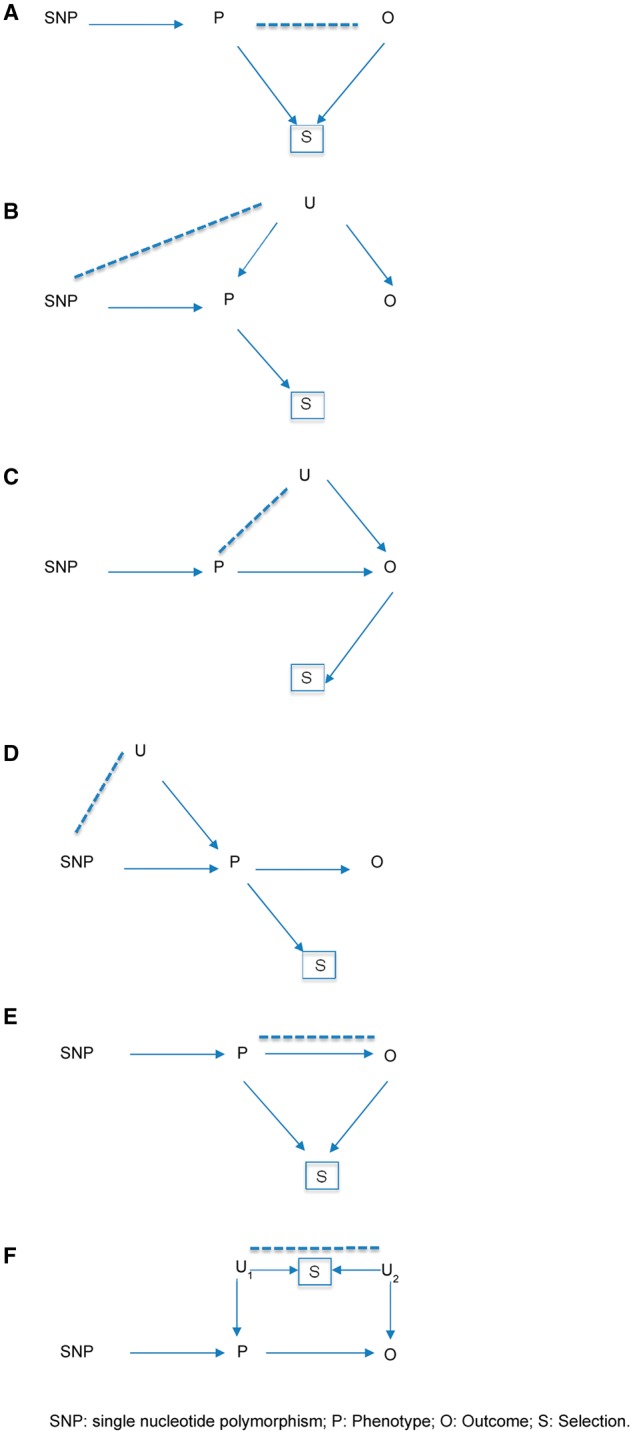
Scenarios where selection bias would occur. A. In truth, the SNP is not causally associated with the outcome; selection will induce an association (which could be positive or negative). B. In truth, the SNP is not causally associated with the outcome; selection will induce an association (which could be positive or negative). C. In truth, the SNP is causally associated with the outcome; selection could make this larger or attenuate it. D. In truth, the SNP is causally associated with the outcome; selection could make this larger or attenuate it. E. In truth, the SNP is causally associated with the outcome; selection will bias this association (which could be positive or negative). F. Note that the association between P and O is biased in the selected sample; however, the association between SNP and O is unbiased in the selected sample. P, Phenotype; O, Outcome; S, Selection; U, Other variables.
