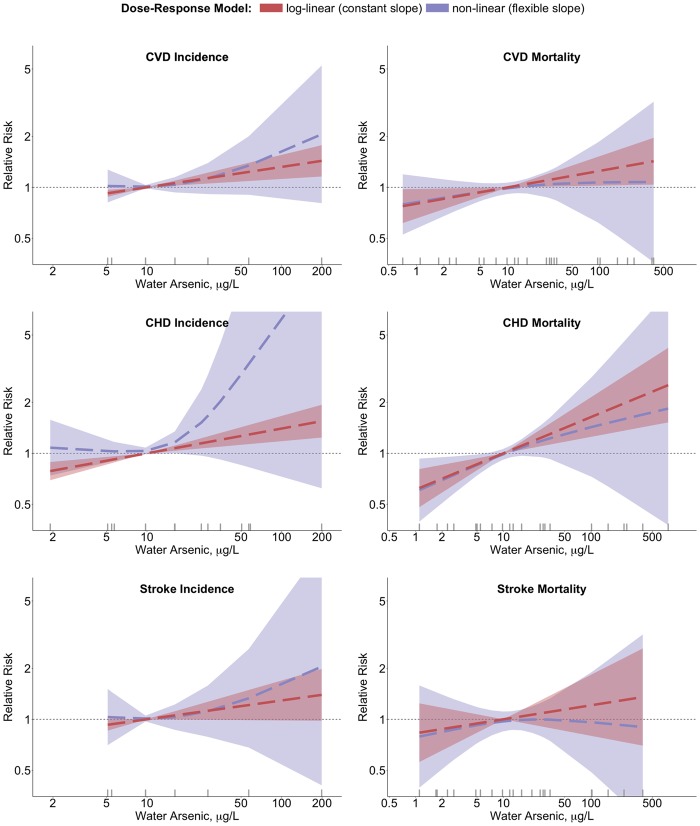
Figure 2.
Pooled log-linear and non-linear relative risks of incident overall cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to estimated water arsenic. Pooled linear (red) and non-linear (blue) relative risks of CVD endpoints (overall CVD, CHD and stroke, stratified by studies of incidence and mortality) were estimated for drinking water arsenic concentrations in reference to 10 µg/l. Dashed lines correspond to pooled relative risks, and shaded regions correspond to the 95% confidence intervals of the pooled relative risks. Log-linear associations were estimated from models with log-transformed estimated water arsenic concentrations. Non-linear associations were estimated from models with restricted cubic splines of log-transformed estimated water arsenic concentrations with knots at the 10th, 50th and 90th percentiles of log-transformed arsenic (exact knot locations vary by model; for CHD incidence, knots were placed at 5.1, 20.5 and 58.7 µg/l). A rug plot along the x-axis provides the median estimated water arsenic concentrations included in each model.