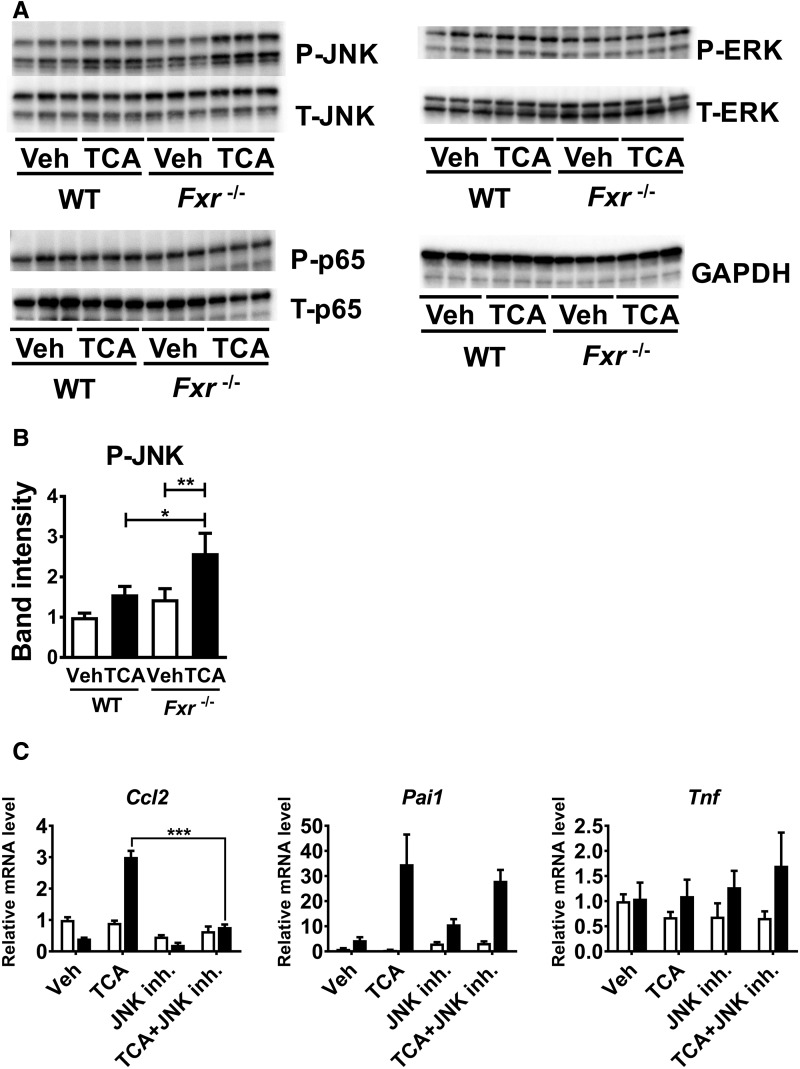
Figure 5.
JNK activation is important for up-regulation of pro-inflammatory modulators by TCA in Fxr-null hepatocytes. A, Primary hepatocytes isolated from Fxr−/− and WT mice were treated with 100 μM TCA or vehicle (Veh) for 6 h. Whole cell lysates (20 μg of proteins) were subjected to immunoblot analysis for determining hepatic levels of total (T-) and phosphorylated (P-) JNK, ERK, and p65. The band of GAPDH was used as a loading control. B, Quantification of P-JNK. The band intensities of P-JNK and GAPDH were quantified using ImageJ software, and the ratio of P-JNK to GAPDH was calculated. Data are presented as the means±SD and two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction was adopted for statistical analysis. *P<.05; **P<.01. C, Primary hepatocytes isolated from Fxr−/− and WT mice were treated with 100 µM TCA or vehicle (Veh) with or without 10 µM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) for 6 h. The mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory modulators were measured. n=3 samples per group. Data are presented as the means±SD and two-tailed Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis; ***P<.001.