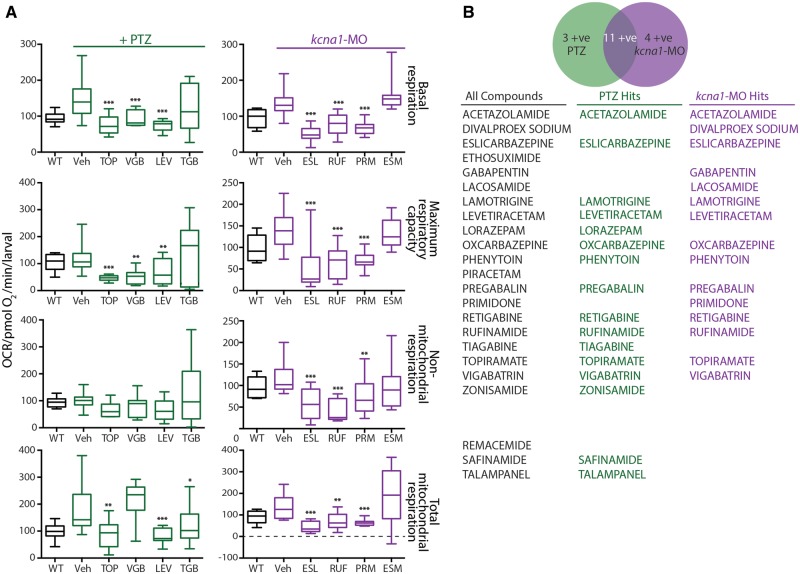
Figure 2.
ASDs are efficacious in zebrafish bioenergetics assays. (A) A double-blinded screen of 20 known ASDs and three compounds that recently failed clinical trials in epilepsy. Thirteen of 20 known ASDs restored elevated basal respiration and total mitochondria respiration to wild-type levels in PTZ-induction model. In the kcna1-MO model, 15 of the 20 known ASDs were efficacious in restoring basal respiration, maximum respiratory capacity and total mitochondrial respiration to wild-type levels. (B) List of the 20 known ASDs and three compounds that recently failed clinical trials in epilepsy used in present study. Two of the three compounds that failed were efficacious in the PTZ-induction but not in the kcna1-MO model. Data in A are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistics are shown comparing treatment group to vehicle control; wild-type and vehicle are statistically different in all graphs although not illustrated; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001 (unpaired t-test); n = 6–7 fish per group. ESL = eslicarbazepine; ESM = ethosuximide; LEV = levetiracetam; PRM = primidone; RUF = rufinamide; TGB = tiagabine; TOP = topiramate; Veh = vehicle; VGB = vigabatrin; WT = wild-type.