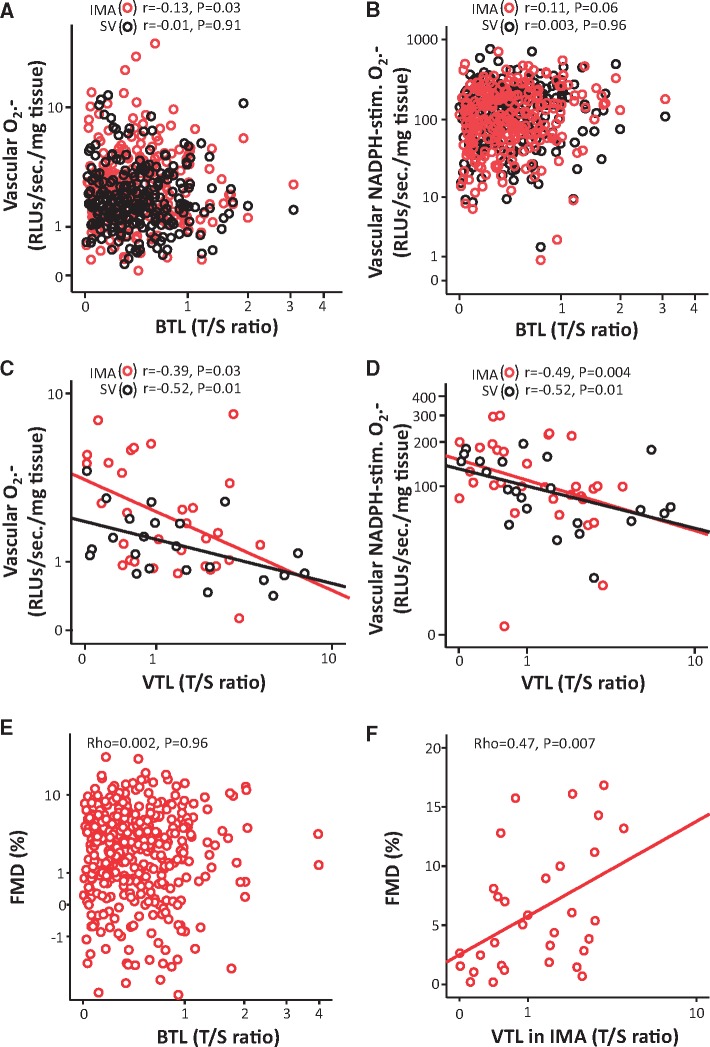
Figure 3.
In the ex vivo arm of Cohort 2, blood telomere length (BTL) was not associated with basal or NADPH-stimulated superoxide (O2.-) in saphenous vein (SV) or internal mammary artery (IMA) segments (A and B). On the contrary, there was an inverse association between vascular telomere length (VTL) and both basal (C) and NADPH-stimulated O2.- (D) in the respective vascular tissue, in a subgroup of 32 IMA & 24 SV. Shortened VTL in IMA was associated with impaired flow mediated dilatation (FMD) of the brachial artery in vivo (F), in contrast with BTL (E).