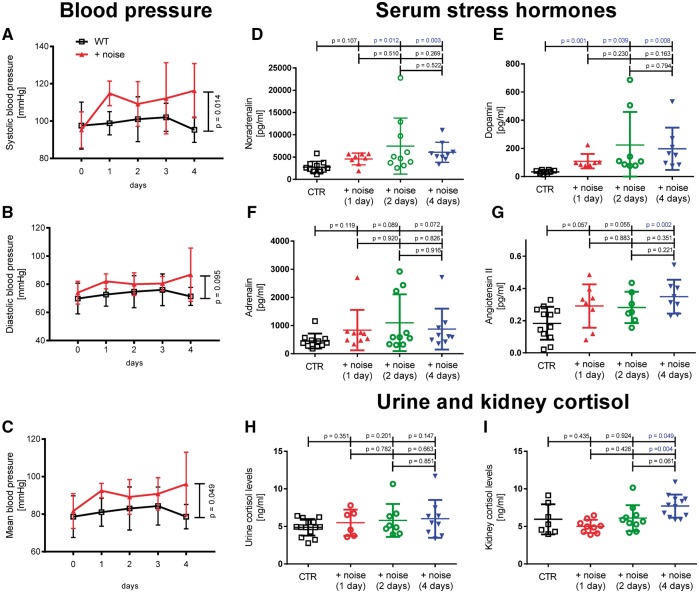
Figure 1.
Effects of noise for 1, 2, and 4 days on blood pressure and stress hormone release. Noise increased significantly systolic and mean arterial (A, C) but not diastolic (B) blood pressure. Noise increased noradrenalin, dopamine and angiotensin II levels significantly and adrenalin by trend (D–G). Cortisol levels in urine and kidney showed a weak trend for an increase under noise exposure, which was significant for kidney cortisol on day 4 (H, I). Data are mean ± SD from n = 8–16 mice/day (A–C), 8–11 (D), 7–8 (E), 9–11 (F), 7–12 (G), 6–14 (H) and 7–12 (I) mice/group.