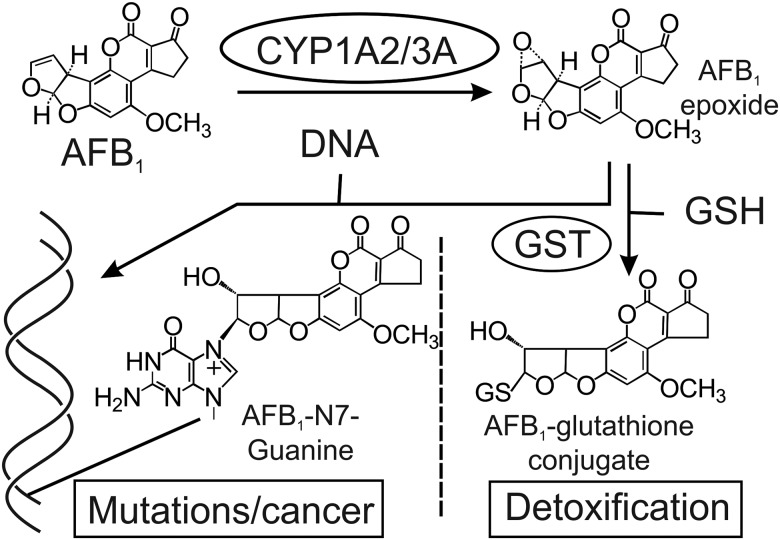
Figure 1.
Overview of AFB1 metabolism. AFB1 is metabolically activated by phase I enzymes, including cytochromes P450 CYP1A2 or CYP3A family members to the reactive AFB1 epoxide, which can damage DNA by forming the AFB1-N7-guanine covalent adduct. The main pathway to detoxify the epoxide involves the phase II enzymes GSTs, which chemically inactivate it by conjugation to GSH (Kensler et al., 2003).