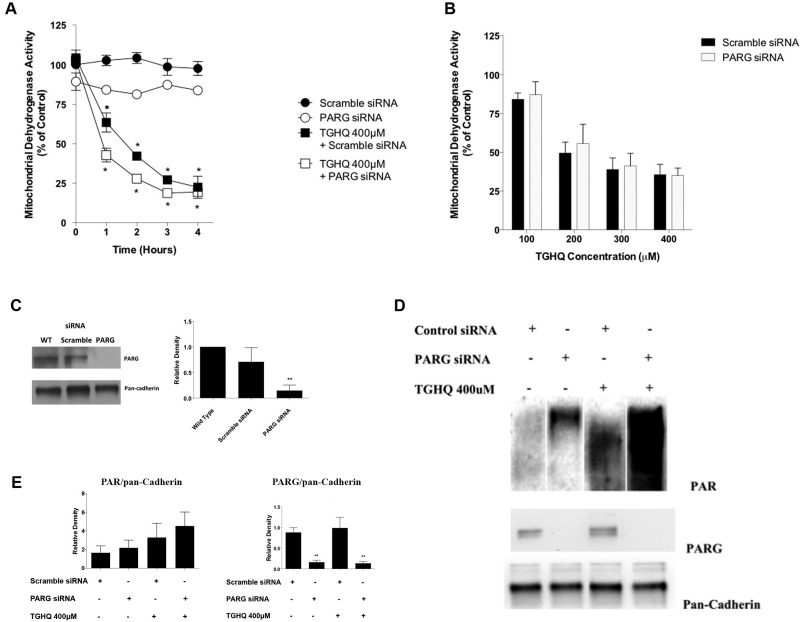
Figure 6.
PARP-1-mediated cell death is independent of PAR processing by PARG. (A) Cells were transfected using 25 nM non-targeting scramble siRNA or PARG siRNA and incubated for 72 h. HK-2 cells were treated with TGHQ 400 μM at various time points (1–4 h). Cell viability was determined using the MTS-based assay. Data are mean ± SE (n ≥ 3) relative to their respective siRNA controls. *P < .05 when compared with control by one-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc Tukey’s test. (B) Cells were transfected using 25 nM non-targeting scramble siRNA or PARG siRNA and incubated for 72 h. HK-2 cells were treated with TGHQ (100–400 μM) in the presence of scramble siRNA or PARG siRNA for 2 h. Cell viability was determined using the MTS-based assay, measuring mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity. Data are mean ± SE (n ≥ 3) relative to their respective siRNA controls. (C) Western blot analysis was performed using anti-PARG, with pan-cadherin as a loading control. **P < .01 when compared with WT by one-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc Tukey’s test. (D) HK-2 cells were treated with TGHQ 400 μM for 30 min in the presence of Scramble siRNA or PARG siRNA. Cells were collected using PAR lysis buffer analyzed by Western blot using anti-PAR antibody, anti-PARG, and pan-cadherin as a loading control. (E) Densitometric and statistical analysis of siRNA knockdown confirmation from three independent experiments. Data are mean ± SE; n ≥ 3. **P < .01 when compared with scramble siRNA by one-way ANOVA followed by a post-hoc Tukey’s test.