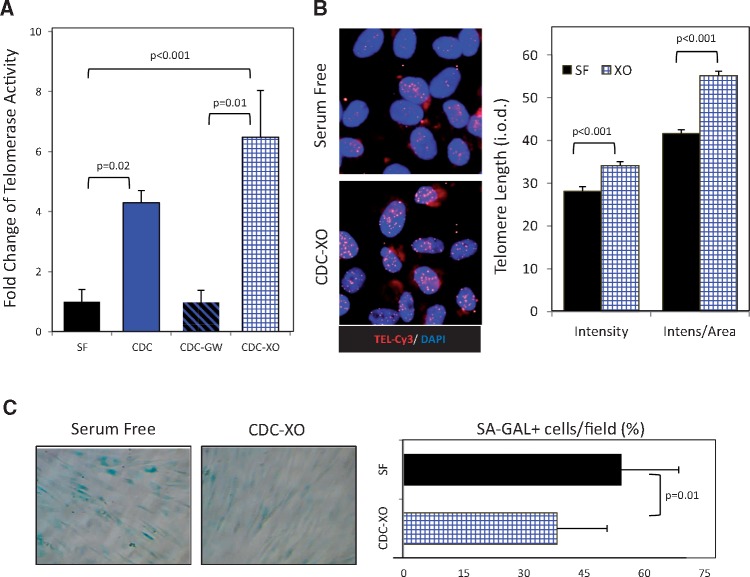
Figure 6.
Exosome-mediated activation of telomerase-telomere axis and decrease of cell senescence by young CDCs in old human cardiac stromal-progenitor cells (CSPCs). (A) Telomerase activity in extracts of CSPCs from old human donors after 96 h was determined following telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) in four groups: the control group incubated with serum-free media (SF); cells co-cultured with young donor CDCs alone or together with GW4869 inhibitor of exosome release (CDC and CDC-GW, respectively), using transwell membranes; cells co-cultured with young CDC exosomes (CDC-XO) resuspended in serum-free media. (B) Representative images of cells subjected to telomere Q-FISH analysis. Nuclei are stained with DAPI and telomeres with specific CY3-labeled probe (red). Telomere length was analysed by measuring the integrated optical density (i.o.d.) of the Cy3-channel within the nuclear borders after subtracting the background i.o.d. Results adjusted to the nuclear area are presented as well. (C) Histochemistry images for senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-GAL) (blue). Proportion of senescent, SA-GAL+ cells after 96 h co-incubation time period with young CDC-XO or SF.