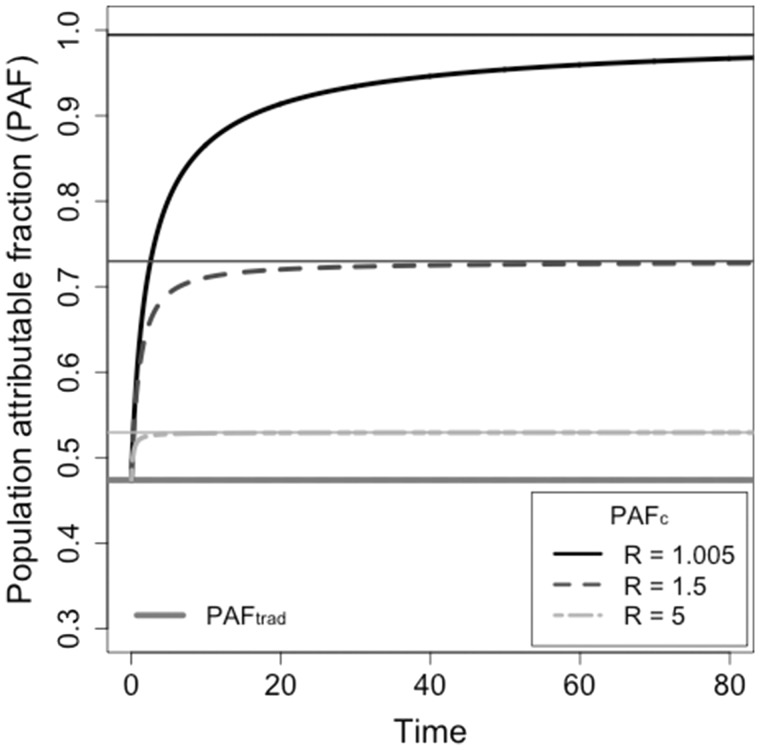
Figure 1.
The relationship between the population attributable fraction (PAF) calculated by simulating epidemics and the basic reproduction number. A risk factor that affects a proportion of the population with relative risk of susceptibility of has a traditional PAF estimate of . Methods for estimating PAF by simulating cumulative incidence with and without a risk factor (PAF) result in estimates ranging from , depending on the basic reproduction number in the general population (the non-risk group). The thick lines illustrate values when for sample reproduction numbers. The thin lines are the asymptotes, given by PAF.