Table 1.
Overview of recent inference methods for the bi-allelic Wright–Fisher model
| Reference | Data | Mut | Mig | Sel | Approach | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markov chain theory | ||||||
| Mathieson and McVean (2013)a | T |
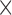
|
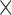
|
Normal | - | |
| Gompert (2015)a | T |
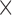
|
Beta | spatpg | ||
| Diffusion approximation | ||||||
| Bollback et al. (2008) | T |
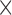
|
Finite-difference | - | ||
| Gutenkunst et al. (2009) | S |
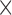
|
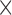
|
Finite-difference |
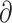 a a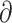 i i |
|
| Lukić and Hey (2012) | S |
|
|
Spectral decomposition | MultiPop | |
| Malaspinas et al. (2012) | T |
|
Numerical approximation | upon request | ||
| Gautier and Vitalis (2013) | S | Spectral decomposition | KimTree | |||
| Steinrücken et al. (2014) | T |
|
|
Spectral decomposition | spectralHMM | |
| Vitalis et al. (2014) | S |
|
|
Stationary DAF | SelEstim | |
| Živković et al. (2015) | S |
|
|
Spectral decomposition | upon request | |
| Ferrer-Admetlla et al. (2016) | T |
|
|
Numerical approximation | ApproxWF | |
| Moment-based approximations | ||||||
| Sirén et al. (2011) | S | Beta | - | |||
| Pickrell and Pritchard (2012) | S |
|
Normal | TreeMix | ||
| Lacerda and Seoighe (2014) | T |
|
Normal | upon request | ||
| Hui and Burt (2015) | T | Beta | NB | |||
| Tataru et al. (2015) | S | Beta with spikes | SpikeyTree | |||
| Terhorst et al. (2015) | T |
|
Normal | EandR-timeseries | ||
The table indicates what type of data the method uses (Data): time series data from one population (T) or single time-point data from multiple populations (S); if the method models new mutations (Mut), migration (Mig) or selection (Sel); which type of approach is used for calculating the DAF (Approach); and whether the method is publicly available (Availability). All methods model genetic drift.
a analyze jointly time series data from multiple populations. The table covers only the more recent inference methods.
