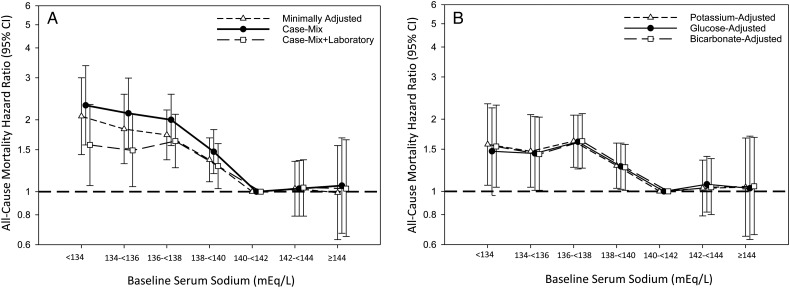
FIGURE 3.
Associations between baseline sodium level and all-cause mortality in minimally adjusted, case-mix and case-mix + laboratory adjusted models (A) and models additionally adjusted for serum potassium, glucose and bicarbonate (B) among incident peritoneal dialysis patients. Minimally adjusted analyses adjusted for entry calendar quarter. Case-mix analyses adjusted for covariates in the minimally adjusted model, as well as age, sex, race/ethnicity, primary insurance, diabetes, alcohol use, congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cerebrovascular disease, human immunodeficiency virus, malignancy, hypertension, atherosclerotic heart disease and other cardiovascular disease. Case-mix + laboratory adjusted analyses adjusted for covariates in the case-mix model, as well as serum albumin, serum creatinine, total iron binding capacity, calcium, ferritin, hemoglobin, iron saturation, renal urea clearance (renal Kt/V), peritoneal urea clearance (peritoneal Kt/V), phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, white blood cell count, automated peritoneal dialysis status at baseline and automated peritoneal dialysis status during follow-up. Case-mix + laboratory + potassium adjusted analyses adjusted for covariates in the case-mix + laboratory adjusted model, as well as serum potassium. Case-mix + laboratory + glucose adjusted analyses adjusted for covariates in the case-mix + laboratory adjusted model, as well as serum glucose. Case-mix + laboratory + bicarbonate adjusted analyses adjusted for covariates in the case-mix + laboratory adjusted model, as well as serum bicarbonate.