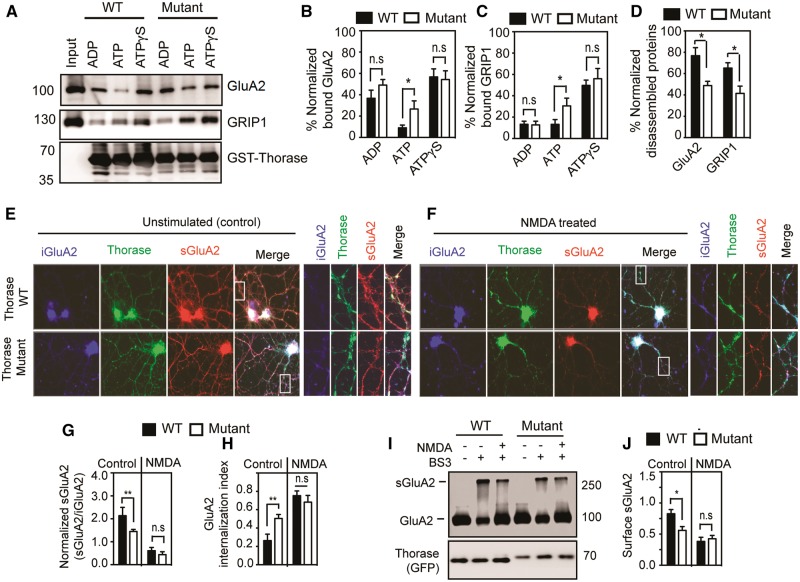
Figure 4.
ATAD1 mutation p.(His357Argfs*15) affects GluA2-GRIP1 complex disassembly and GluA2 surface expression. (A) Immunoblot analyses of GST-Thorase pulldown of the GluA2-GRIP1 complex from Thorase knockout whole brain lysate in the presence of different nucleotides (ATP = hydrolysable ATP; ATPγS = non-hydrolysable ATP). The samples were incubated at 4°C for binding and then at 37°C for ATP hydrolysis to trigger the disassembly of the protein complex. (B and C) The graphs represent normalized per cent bound GluA2 (B) and GRIP1 (C) in the GST-Thorase pulldown samples for A. (D) Normalized percentage of GluA2 and GRIP1 disassembled from Thorase-GluA2-GRIP1 complex in A. (E and F) Representative immunofluorescence images of unstimulated and NMDA-induced endocytosis of GluA2 in Atad1−/− neurons expressing Thorase-GFP wild-type (WT) or the mutantHis357Argfs*15 (Mutant). (G) Normalized ratio of surface GluA2 (sGluA2) to internalized GluA2 (iGluA2) for E and F. (H) GluA2 internalization index measured as the ratio of iGluA2 to the total GluA2 (iGluA2 plus sGluA2) fluorescence intensities. (I) Immunoblot analyses of BS3-crosslinking of sGluA2 in Atad1−/− neurons expressing Thorase-GFP wild-type or mutantHis357Argfs*15. (J) The normalized optical densitometry quantification of sGluA2 for I. Mean ± SEM of three experiments performed in triplicate. n = 3, **P < 0.05, *P < 0.10, n.s. P > 0.10, ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post hoc test when compared with wild-type.