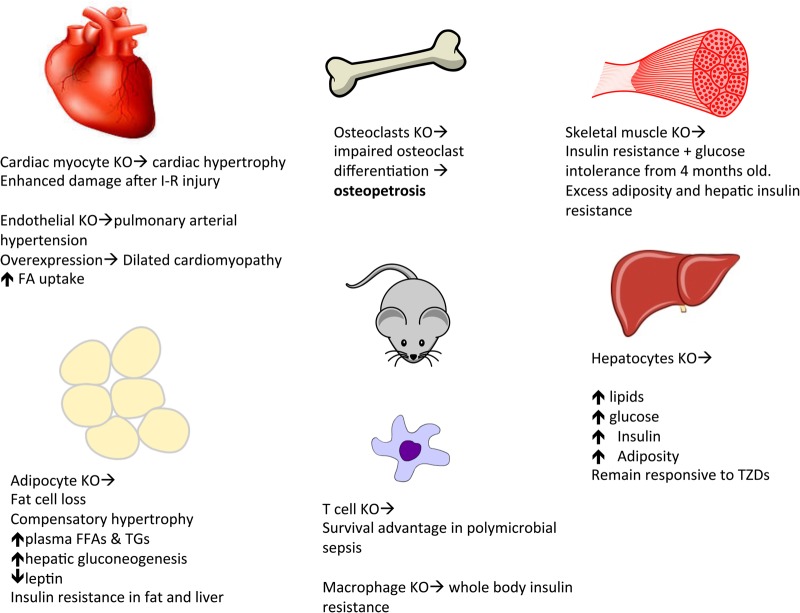
FIGURE 2.
Tissue-specific knockout (KO) of PPAR-γ: skeletal muscle [29], hepatic [30], cardiac I-R (ischaemia–reperfusion injury) [31]; adipose [32]. Osteoclasts: Tie2Cre/flox mouse model (specific PPAR-γ gene deletion) [27], endothelial cells [33], T cells [34]. In the liver of the ob/ob mouse (genetically predestined to obesity) and the lipoatrophic mouse (AZIP) examples, KO of PPAR-γ has been shown to remedy the associated hepatic steatosis [35] but at the same time worsen the triglyceride clearance and total body insulin resistance.