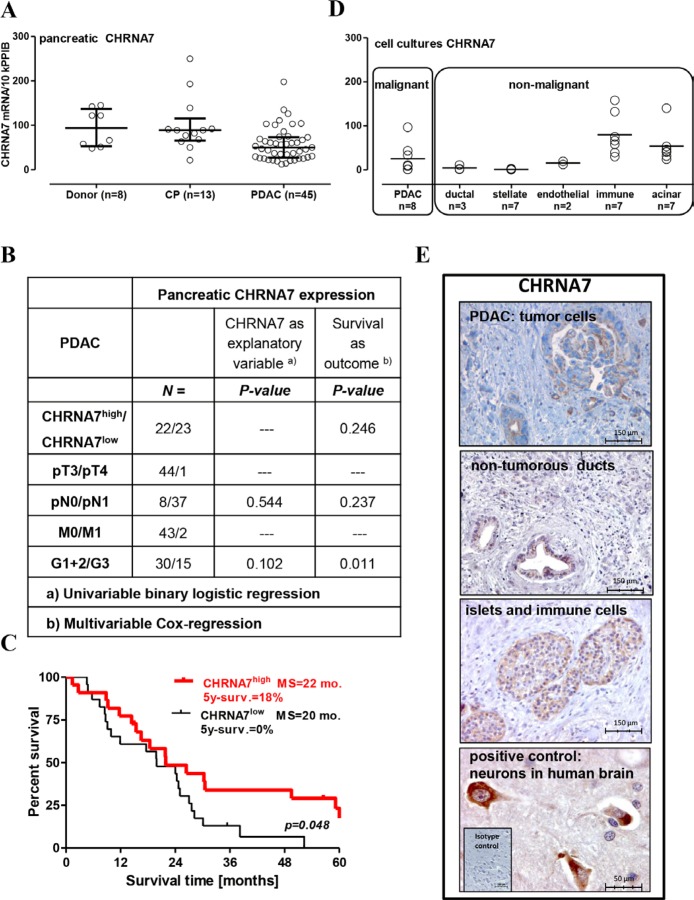
Figure 1. Preservation of CHRNA7 expression in the pancreas is associated with better prognosis for operable PDAC patients.
(A) CHRNA7 mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR in 66 pancreatic samples obtained from the organ donors and patients with chronic pancreatitis (CP) or pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC). The groups were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test (p = 0.004) with Dunn’s procedure, which established significant down-regulation of CHRNA7 in PDAC patients (p < 0.05). (B) Pancreatic CHRNA7 mRNA expression is not associated with tumor size, metastasis to lymph nodes, or differentiation grade. (C) Dividing the PDAC patients with resected tumors into CHRNAhigh/low groups according to the mRNA level in the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed longer survival in the CHRNAhigh group (cut-off = 50 transcripts/10k PPIB; log-rank test p = 0.048), MS: median survival. (D) Specific contribution of the major cell types populating cancerous pancreatic lesion to overall CHRNA7 mRNA expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR analysis of the primary cell cultures (acinar, stellate/stromal, immune) and established cell lines (endothelial HUVEC/HMDEC, pancreatic ductal normal HPDE and tumor AsPC-1, BxPC-3, Capan-1, COLO357, MiaPaca2, PANC-1, SU.86.86, T3M4). (E) Immunohistochemical analysis located the CHRNA7 protein in pancreatic islets, immune cells, normal ducts, and cancer cells. Neuronal staining in human brain tissue served as a positive control.