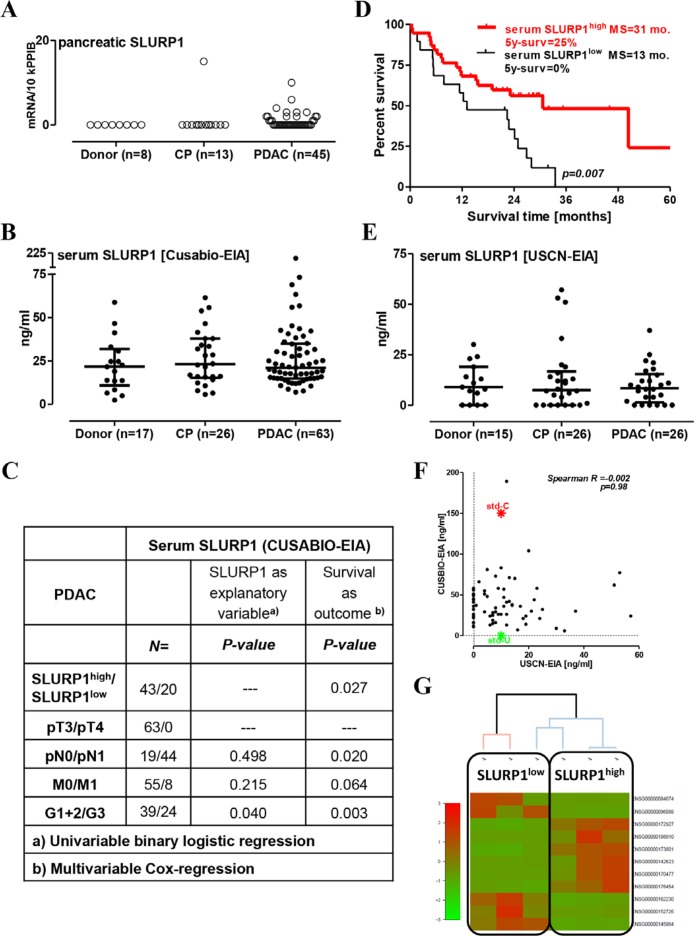
Figure 2. High level of circulating SLURP1 is associated with better survival in operable PDAC patients.
(A) The measurement of pancreatic SLURP1 mRNA expression with qRT-PCR in 66 pancreatic samples revealed the lack of expression in non-malignant pancreatic tissues and most PDAC lesions. (B) The concentration of SLURP1 was measured in 106 human serum samples using a commercial EIA kit produced by CUSABIO. Multiple comparison testing revealed a lack of difference between the analyzed groups (p = 0.643). (C) Circulating SLURP1 levels correlated with the grade of differentiation but not with any of the TNM parameters. (D) Dividing the PDAC patients with resected tumors into SLURP1high/low groups according to the preoperative level of circulating SLURP1 for the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed significantly longer survival of SLURP1high patients (cut-off = 16 ng/ml; log-rank test p = 0.007), MS: median survival. (E) The concentration of SLURP1 was re-measured in 67 human serum samples using a commercial EIA kit produced by USCN and confirmed the lack of difference between the analyzed groups (p = 0.951). (F) Nevertheless, the USCN-EIA recognized the CUSABIO standard but not vice versa, and the USCN values for SLURP1 were three-fold lower and lacked any correlation with the CUSABIO values. Additional information is presented in Table 1. (G) Clustering analysis of the RNAseq data obtained for the PDAC specimens corresponding to the serum samples with low and high SLURP1 content.