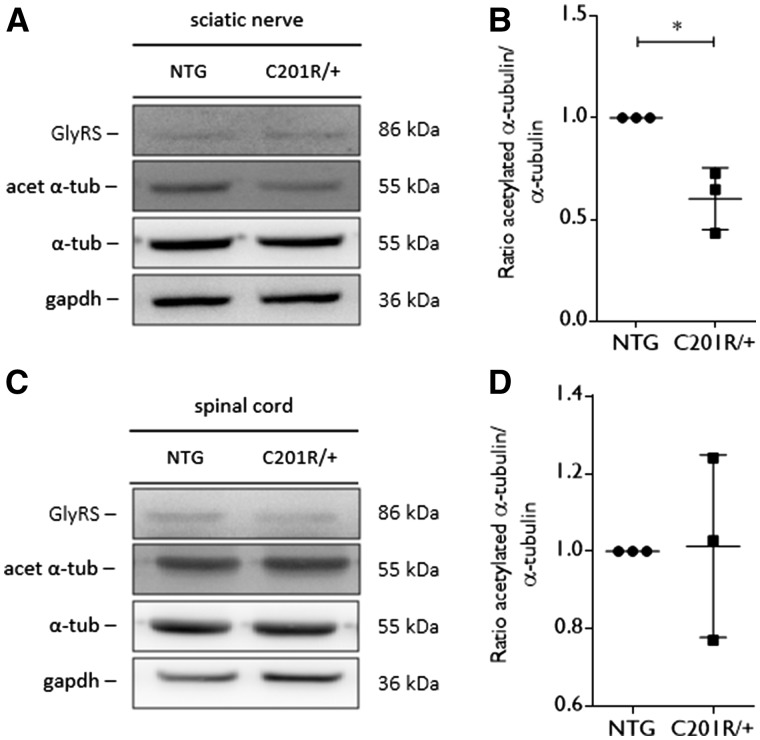
Figure 4.
Acetylated α-tubulin levels are altered in peripheral nerve tissue from GarsC201R/+ mice. (A) Western blot analysis was used to determine the acetylation status of α-tubulin in tissue homogenates from GarsC201R/+ and littermate control mice (non-transgenic, NTG). An antibody directed against GlyRS was used to assess GlyRS expression levels. GAPDH expression levels were used as a control for equal sample loading. (B) The amount of acetylated α-tubulin compared to the total α-tubulin levels was quantified by densitometry and the values were normalized to the non-transgenic samples: non-transgenic 1.00 ± 0.00, n = 3 samples versus GarsC201R/+ 0.60 ± 0.15 ms, n = 3 samples; unpaired t-test: t = 4.518, P = 0.0107. (C) The level of acetylated α-tubulin was detected by western blot analysis in tissue homogenates from spinal cord from GarsC201R/+ and littermate control (non-transgenic) mice. GlyRS expression levels were checked and GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) The ratio between acetylated α-tubulin and total α-tubulin was quantified by densitometry and values were normalized to non-transgenic samples. n = 3 mice.