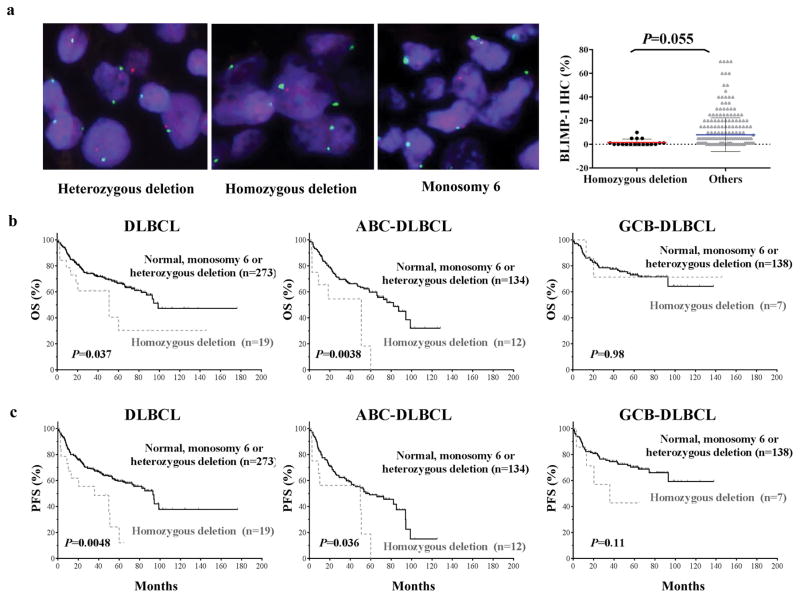
Figure 1.
Homozygous PRDM1 deletion in DLBCL cases. (a) Representative examples of FISH results with heterozygous PRDM1 deletion (of note are a mixture of cells with two green signals, corresponding to centromere 6, but lacking red signals, corresponding to PRDM1, and cells with two green signals and one red signal), homozygous PRDM1 deletion (of note are two green signals but a lack of red signals in the majority of the cells; one cell in the center of the microphotograph has both red and green signals and serves as an internal positive control), and monosomy 6 (all cells have only one green and one red signal). DLBCL patients with homozygous PRDM1 deletions had lower levels of BLIMP-1 protein expression than did the rest of the studied patients. (b–c) The impact of homozygous PRDM1 deletion on OS and PFS in all patients with DLBCL, patients with ABC-DLBCL, and patients with GCB-DLBCL. Patients with this deletion had shorter OS and PFS durations than did patients with normal FISH signals, heterozygous PRDM1 deletions, or monosomy 6. This trend was greater in patients with ABC-DLBCL than in GCB-DLBCL.