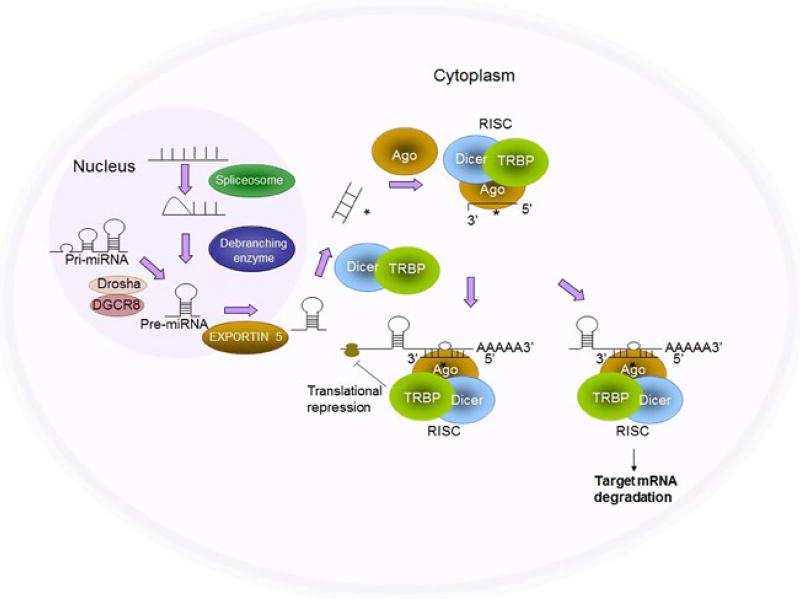
FIGURE 1.
Biogenesis of miRNAs. RNA polymerase II transcribes miRNA genes, generating long primary transcripts (pri-miRNAs). In the nucleus, the RNase III-type enzyme Drosha processes the long primary transcripts (pri-miRNAs), yielding hairpin precursors (pre-miRNA). Exportin 5 transports the pre-miRNAs from the nucleus into the cytoplasm. The pre-miRNA hairpins are further processed by Dicer into mature miRNAs, which are incorporated into the Argonaute (Ago) protein and form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) together with Dicer. Once incorporated into the RISC, the miRNAs then guide the RISC to the target genes and repress target gene expression by destabilizing the target mRNAs or suppressing protein translation (Refer to our paper [50])