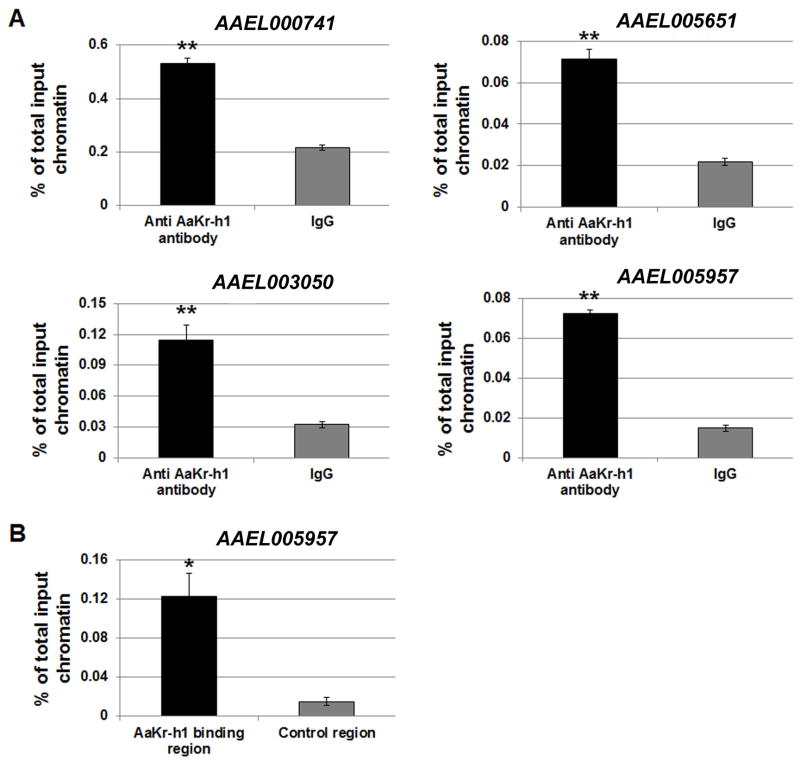
Figure 3.
Verification of the in vivo binding of AaKr-h1 to the DNA sequences that were identified by ChIP-cloning. (A) Enrichment of four sequences was confirmed in an independent ChIP assay using mosquito abdomens collected at 48 h PE. The AaKr-h1 antibody and rabbit IgG (as control) were used in this ChIP experiment. Real-time PCR was performed to compare the enrichment of the AaKr-h1 binding sequences between the immunoprecipitations with the AaKr-h1 antibody and with rabbit IgG. (B) Selective binding of AaKr-h1 to the regulatory region of AAEL005957. After chromatin immunoprecipitation with the AaKr-h1 antibody, the precipitated DNA was analyzed using real-time PCR to compare the enrichment of the regulatory region identified by ChIP-cloning and a control region in the coding sequence of AAEL005957. Results are shown as a percentage of input chromatin and represent mean value ± S.D. of three replicates. Statistical analysis was conducted using a paired t-test (**, p<0.01; *, p<0.05).