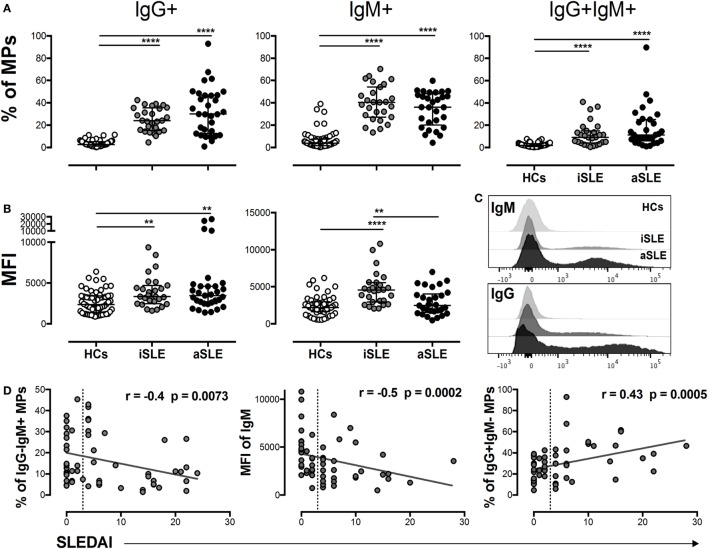
Figure 2.
MPs-IgG + are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) activity. (A) Frequency of circulating MPs-IgG + IgM−, MPs-IgG − IgM +, and MPs-IgG + IgM + in patients with inactive SLE (iSLE) (n = 28), patients with active SLE (aSLE) (n = 32), and healthy controls (HCs) (n = 60). (B) MFIs of IgG and IgM on circulating microparticles (MPs). (C) Representative histograms show IgM (upper) and IgG (lower) expression on MPs from patients with aSLE (black), patients with iSLE (dark gray), and HCs (light gray). (D) Analysis of the correlations between the MPs-IgG−IgM +, MPs-IgM + MFI, and MPs-IgG + IgM− frequencies and systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) scores. Comparisons among groups were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s post hoc test; **p ≤ 0.01 and ***p ≤ 0.001. Correlation analyses were performed by determining Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients and 95% confidence intervals; the dotted line indicates the cut-off point between patients with iSLE (SLEDAI < 4) and those with aSLE (SLEDAI ≥ 4).