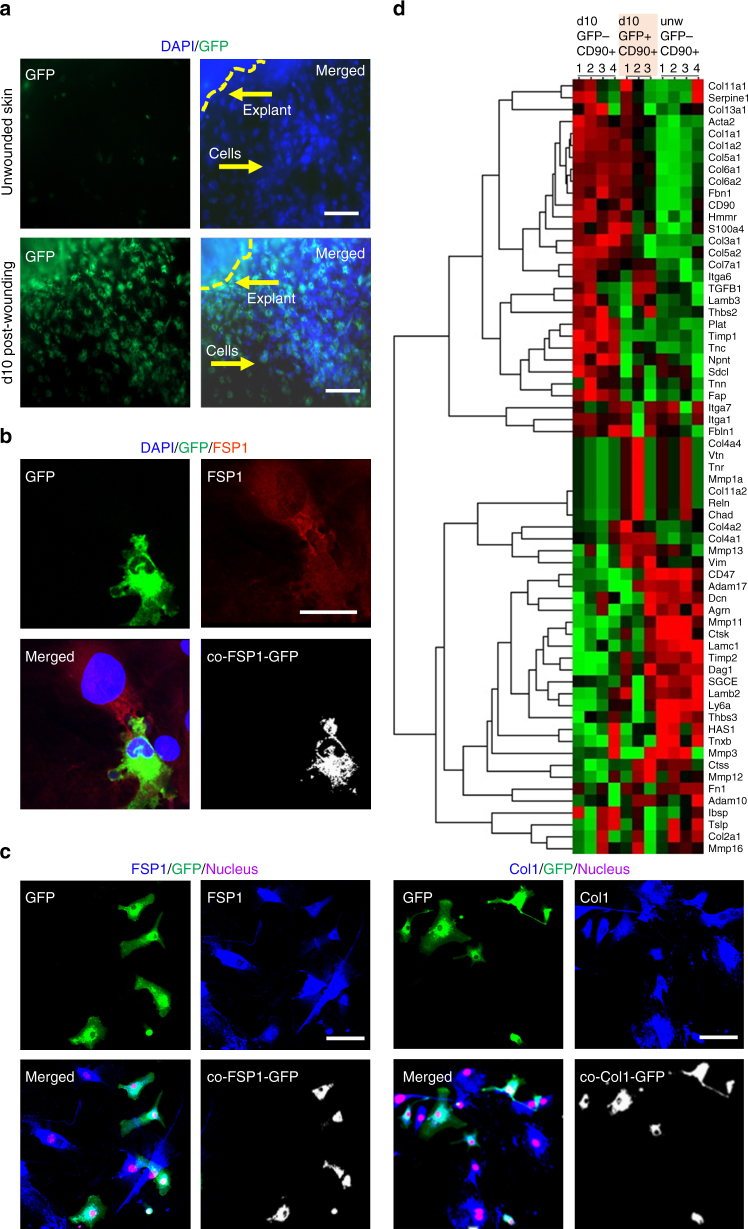
Fig. 4.
Isolation of macrophage-derived fibroblast-like cells from wound-derived explants. a Primary dermal fibroblasts isolated from skin or d10 post-wounding tissue of LysMCreRosamT/mG mice. Scale bar = 50 µm. b GFP+ FSP+ fibroblasts interlinked with GFP− FSP+ fibroblast isolated from d10 wound explants. Scale bar = 20 µm. c (left) Immunostaining of GFP+ (myeloid, green) and FSP1 (fibroblast, blue) cells in d10 wound explants skin cultures n = 5, scale bar = 50 µm. Colocalization of the GFP+ cells (green) with FSP1+ (blue) demonstrating their myeloid origin. (right) Immunostaining of GFP + (myeloid, green) and Col1 (fibroblast, blue) cells in d10 wound explants skin cultures n = 5, scale bar = 50 µm. Multiple fibroblast-specific staining (FSP1/Col1) demonstrated the purity (>99%, fibroblasts) of the explant culture. d Heat map illustrating clusters of transcripts from GFP−CD90+ or GFP+CD90+ primary fibroblasts isolated from d10 wound explants. Additionally, GFP-CD90+ primary fibroblast were isolated from unwounded skin. Gene expression profiling of 70 genes relating to ECM/fibroblast was performed using NanoString nCounter system. The expression pattern of GFP−CD90+ or GFP+CD90+ primary fibroblasts from d10 wound explants were largely similar, i.e., not significantly different (t-test with Bonferroni correction) but was distinctly different from unwounded skin GFP-CD90+ primary fibroblasts