Abstract
Transcriptional riboswitches modulate downstream gene expression by a tight coupling of ligand-dependent RNA folding kinetics with the rate of transcription. RNA folding pathways leading to functional ON and OFF regulation involve the formation of metastable states within well-defined sequence intervals during transcription. The kinetic requirements for the formation and preservation of these metastable states in the context of transcription remain unresolved. Here, we reversibly trap the previously defined regulatory relevant metastable intermediate of the Mesoplasma florum 2′-deoxyguanosine (2′dG)-sensing riboswitch using a photocaging-ligation approach, and monitor folding to its native state by real-time NMR in both presence and absence of ligand. We further determine transcription rates for two different bacterial RNA polymerases. Our results reveal that the riboswitch functions only at transcription rates typical for bacterial polymerases (10–50 nt s−1) and that gene expression is modulated by 40–50% only, while subtle differences in folding rates guide population ratios within the structural ensemble to a specific regulatory outcome.
Riboswitches are RNA-based regulatory elements, which regulate downstream gene expression by binding of small molecular weight ligands. Here the authors demonstrate the molecular mechanism of a transcriptional riboswitch that integrates changes in transcription rates, metabolite concentration, and kinetic on- and off-rates of ligand binding.
Introduction
Riboswitches selectively bind metabolites to control the transcription or translation of metabolite-associated genes. In general, riboswitch function is described as a ligand-dependent switch between two mutually exclusive conformations to either permit or repress gene expression1,2. For riboswitches that regulate gene expression on the level of translation, reversible conformational switching allows RNAs to adopt distinct ligand-dependent functional folds at equilibrium during multiple rounds of translation. As a consequence, RNA synthesis and the cellular response to changes in metabolite concentration are separated in time. The functional relevant switch underlying translational riboswitches modulate ribosome access to the SD sequence3–6, but also more complex regulation mechanisms have been discovered7.
In contrast, control of gene expression by premature termination of transcription inevitably requires temporal coupling of RNA synthesis and conformational switching. Riboswitches utilize rho-independent transcriptional termination8,9. Under these conditions, the nascent transcript can either adopt a sequence-conserved terminator conformation that disrupts the polymerase complex or form one or several alternative, so-called antiterminator conformations that avoid termination. The metabolite concentration EC50, at which riboswitches operate, often exceeds the KD values for ligand binding by at least one order of magnitude3,10–14. This observation indicates that fast folding of functional states during well-defined transcription intervals is important for riboswitch function.
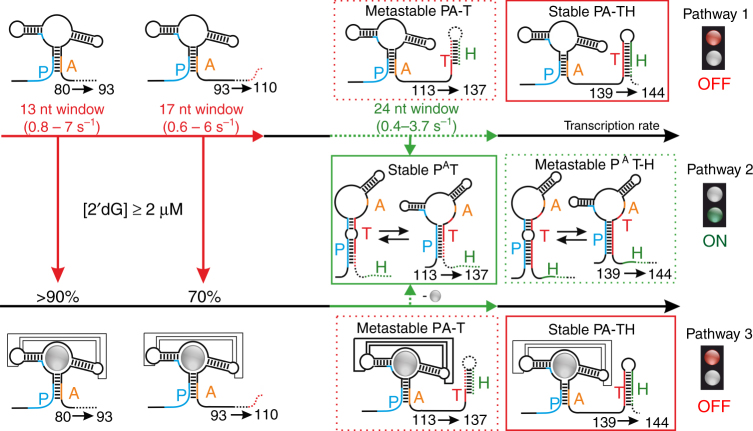
In a previous study, we investigated the landscape of the thermodynamically stable states adopted in either the presence or absence of metabolite for mRNA transcripts of increasing chain length15. The ligand-dependent conformational rearrangement underlying riboswitch function typically involves four distinct sequence segments P, A, T, and H as depicted in Fig. 1. In the 2′dG riboswitch, an mRNA containing 80 nucleotides is the first transcript that can form the interaction between strands P and A. Ligand binding can occur directly after the aptamer domain is transcribed. Interestingly, ligand can also bind to the growing mRNA up to nucleotides 80–113 nt, but the stability of these mRNA-ligand complexes and thus the population of ligand-bound states continuously decrease during the addition of nts 90–113 from >90% to 70%. As strand T is transcribed, the PA interaction becomes metastable (PA–T) in both the ligand-bound and ligand-free form. In the equilibrium model, folding from PA–T to the antiterminator conformation PAT concomitantly occurs during transcription of nucleotides 113 to 137. Previous studies assume ligand binding within the first transcription interval (nts 80–110) to stabilize the PA interaction sufficiently to inhibit an interaction with strand T and to ensure OFF function, but it remains uncertain how the PAT state is selected from only one metastable state in the context of transcription. PAT states adopted within the second transcription interval (in green) become metastable as strand H is transcribed (PAT–H) during synthesis of nts 139 to 144 in both, absence or presence of ligand. Within this short period during transcription, the terminator conformation PA–TH represents the most stable state. It follows that deciphering the change of kinetics of antiterminator formation (PAT) depending on the absence and presence of ligand represents the most important information regarding regulation.
Fig. 1.
Non-equilibrium model for the co-transcriptional conformational switch of the 2′dG-sensing riboswitch. Regulatory function by transcriptional riboswitches is based on a ligand-dependent interplay between the four sequence segments P (5′-aptamer strand), A (aptamer-stabilizing strand), T (switching strand), and H (terminator strand)15. Previously derived transcription intervals for folding events involving a stabilization of the aptamer domain via the P–A interaction or switch in strand interaction (A–T interaction) are highlighted in red (ligand binding) and green (ON state folding), respectively. Directly after transcription of the aptamer domain, 2′dG can bind during the synthesis of nts 80–110 (30 nt window), with a continuous decrease in the ligand binding efficiency from >90% to 70% between nucleotides 93 and 110. Continuation of transcription beyond nt 113 transforms both the ligand-bound and ligand-free aptamer domains (PA–T) into metastable states (dashed red box). Folding to the regulatory ON state (PAT, solid green box) can only occur during synthesis of nucleotides 113–137. At the regulatory decision point, folded PAT–H states are metastable (dashed green box), while the PA–TH conformation (solid red box) represents the lowest free energy state in both absence and presence of ligand. Metastable states are highlighted by dashed boxes and lowest free energy states by solid boxes
According to the equilibrium model, the effects of ligand binding on the overall fold adopted at a specific transcript length is insignificant. Rather, formation of metastable intermediate states as important navigators of the regulatory outcome suggests a correlation between the life times of these states and transcription rates to be critical for riboswitch function. Here, we unravel these kinetic requirements to achieve and to maintain a ligand-dependent reversal of population ratios of functional OFF and ON states during transcription. On the example of the central metastable PA–T conformation of the 2′dG riboswitch, we demonstrate that ligand binding does not induce major changes in equilibration kinetics of the PA–T state, but slows refolding to allow the polymerase to bypass the metastable transcription barrier for the majority of nascent transcripts.
Results
Reversible trapping of the metastable PA–T conformation
To monitor antiterminator (PAT) folding, we trapped the PA conformation of the 121 mer transcriptional intermediate by incorporating photolabile protection groups in strand T. These protection groups prevent antiterminator helix PT formation and allow monitoring of folding from PA to PT after photolysis by light-induced real-time NMR as reported previously16–18. The 121 nt transcriptional intermediate forms a complete antiterminator helix PT at equilibrium. While refolding from PA–T to PAT is initiated at nucleotide 113, segment 113–121 only contains four weak base pairs within helix PT, and, therefore, refolding kinetics from PA–T to PAT are most accurately described at length 121 on average.
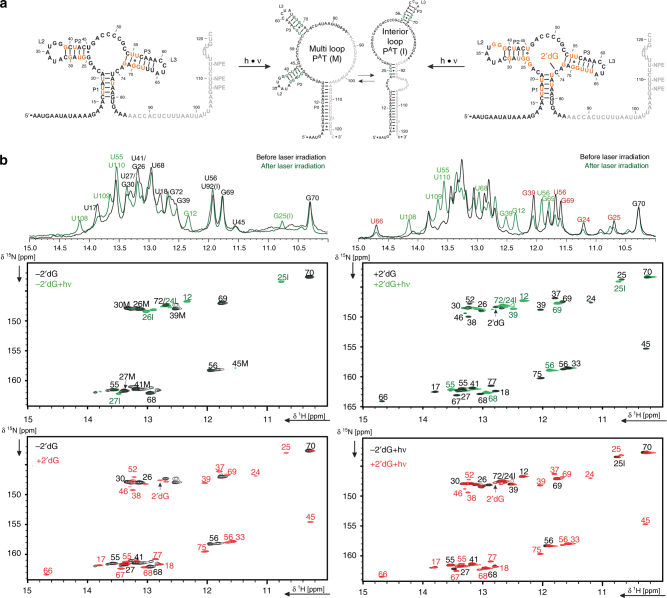
Photocaged dGsw121 (dGsw121,caged) was prepared by enzymatic splinted ligation and contained three NPE protection groups at the C4 atoms in the nucleobases of Uracil residues 108, 110, and 112 (Fig. 2a, Supplementary Fig. 1). In addition to steric hindrance, these NPE protection groups introduce a tautomeric shift at the Watson–Crick base pairing site to prevent base pairing. The RNA fragment comprising nucleotides 1–85 was transcribed in 15N-G/U isotope labeled form. The NPE-protected smaller fragment comprising nucleotides 86–121 was chemically synthesized (Supplementary Fig. 2, Table 1). We analyzed dGsw121,caged by NMR-spectroscopy to verify that trapping the PA fold in the caged construct was successful. Figure 2b shows an overlay of NMR spectra before and after photolysis, while in the 15N-correlation spectra only the 15N-labeled fragment (nts 0–85) is detectable. In dGsw121,caged, the conformation of the aptamer domain (PA–T) is maintained as evidenced by characteristic imino proton reporter signals, in particular U17 and U1819. Irradiation at 355 nm releases native dGsw121 and subsequently induces formation not of a single, but of two interconverting antiterminator conformations (PAT(I)) and (PAT(M)), identified by helix PT reporter signals G12, U108, U109, and G25I. In the presence of ligand, the antiterminator conformations PAT folds only to ~80%, in agreement with the static experiments15. In the ligand-free form, chemical shifts of helices P2 and P3 are identical in either the aptamer PA or antiterminator PAT conformations, while those signals can be distinguished in the ligand-bound form due tertiary interactions induced by ligand binding.
Fig. 2.
Structural integrity of caged dGsw121 before and after laser irradiation. a Secondary structures of dGsw121 in presence and absence of ligand, before photolysis (PA–T) and after photolysis to form the antiterminator conformations PAT(M) and PAT(I). Aptamer domain imino protons detectable by NMR are highlighted in orange. Antiterminator imino protons detectable by NMR are highlighted in green. b Overlay of 1D NMR spectra of caged dGsw121 before (black) and after (green) laser irradiation in absence (left) and presence (right) of 2 eq. of ligand and combinations of overlay of 1H,15N -TROSY of dGsw121 in absence (−2′dG) or presence of 2 eq. ligand ( + 2′dG), and before and after ( + hν) laser irradiation. The spectra were recorded on 100 µM NMR samples with 6 eq. of Mg2+ at 800 MHz and 298 K. Characteristic imino proton signals to monitor the formation of PAT are highlighted in green. Characteristic imino proton signals to monitor aptamer dissociation in the presence of ligand are highlighted in red
Life times of the metastable PA–T state by real-time NMR
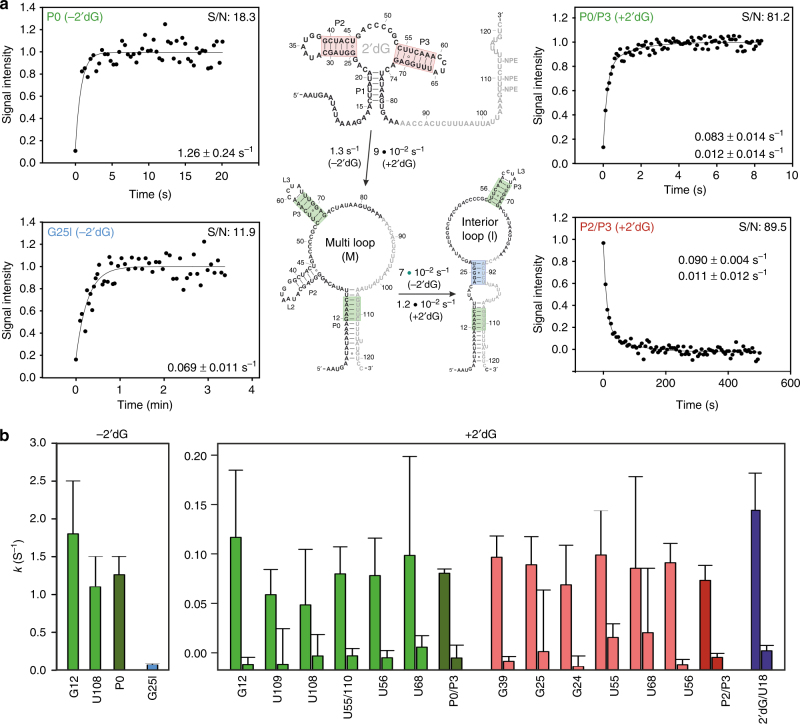
We obtained kinetic traces by real-time NMR at the physiological temperature of the bacterium M. florum (25 °C). Rates for individual base pairs were determined (Supplementary Fig. 3), utilizing F-statistics to check for statistical significance (Supplementary Table 2). Rapid formation of PAT in the absence of ligand required averaging of transients obtained from individual imino protons to yield a final rate for helix formation with improved accuracy (Fig. 3a). We can confirm the validity of this approach by the larger number of kinetic traces with improved S/N obtained for the ligand-bound form (Fig. 3b), where the average rate for helix P2/P3 formation accurately reflects rates of individual bases. In the absence of ligand, PAT(M) folds at a rate of ~1.3 s−1. The second conformation PAT(I) could be monitored by the characteristic and isolated signal G25I, and folds at 10-fold slower rates of 7*10−2 s−1. In the ligand-bound form, the difference in chemical shift of helices P2/P3 in PA–T and PAT allows monitoring of aptamer dissociation in addition to PT formation. The ligand-bound PA conformation folds to PAT(M) at rates of ~9*10−2 s−1 with a second slower rate in the order of ~1*10−2 s−1, which we assign to re-equilibration to PAT(M) after formation of PAT(I).
Fig. 3.
Kinetic traces for ON state folding. a Averaged kinetic traces for antiterminator PAT(M) formation in presence and absence of ligand (green), kinetic trace for antiterminator PAT(I) formation derived from the imino proton reporter signal G25I (blue), and averaged kinetic trace for aptamer dissociation in the presence of ligand (red). Dissociation and association of helical segments monitored by real-time NMR are color coded accordingly in the secondary structure depiction on the right. b Individual rates derived from transients shown in (a) and Supplementary Fig. 3. Green bars indicate rates of P0 and P3 formation in PAT(I) and PAT(M) conformations, with the dark green bar corresponding to averaged rates for complete helix formation. The blue bar shows kinetic rates for PAT(I) formation only. Red bars correspond to helix P2 and P3 dissociation in the ligand-bound state and dark red to the averaged dissociation of helix P2 and P3. The purple bar corresponds to cooperative dissociation of both the ligand 2′dG and U18 (P1). Errors correspond to the s.d. of the fit. S/N values shown correspond to the S/N ratio of the latest data point
The analysis of the kinetics reveals three relevant functional pathways as depicted in Fig. 1. Folding of PAT(M) in the absence of ligand (pathway 2) is on the same timescale (1.3 s−1) as bacterial polymerases require to synthesize the subsequent 24 nucleotides (0.4–3.7 s−1)20–23. The synchronization of transcription with folding rates that are unimolecular and thus concentration independent and sufficiently long life-time of the metastable state ensures ON state function. In contrast, ligand binding slows down folding from the PA conformation to the PAT(M) conformation to a rate of ~0.1 s−1, and, thus, below transcription rates (pathway 3). Hence, in the presence of ligand, antiterminator formation for transcript length for which it represents the stable fold (113–137 nts) is too slow, and, thus, OFF state function is triggered. Further, equilibration between PAT(M) and PAT(I), occurs on the same timescale as antiterminator formation in the presence of ligand, and, therefore, cannot compete with transcription rates. Therefore, our kinetic experiments reveal that only one of the two antiterminator conformations (PAT(M)) represents the regulatory decisive ON state, and, thus, demonstrate a kinetic selection of only a single functionally relevant conformation in the structural ensemble.
Ligand binding kinetics
OFF state function depends on ligand binding kinetics and subsequent RNA folding. We further determined the kinetics for transcripts of different chain length by stopped-flow spectroscopy with a surrogate fluorescence ligand 2-aminopurine 2′-deoxyriboside (2′dAP) to investigate whether the ligand association rates (kon) remain constant within the relevant transcription interval. To facilitate binding of 2′dAP, the ligand selectivity was shifted from G to A by mutating the Watson–Crick ligand recognition site C74 to U74 (dGswC74U), a common approach applied for purine riboswitches (Fig. 4a)24,25. Homogeneous binding of 2′dAP to dGswC74U was verified by NMR and kon rates were obtained for 9 different transcriptional intermediates (Supplementary Fig. 4 and Table 3). The results show that ligand binding kinetics are virtually identical for constructs that adopt a stable PA fold based on static measurements (Fig. 4b, transcript lengths 80–113 nt). Truncated P1 constructs as well as antiterminator constructs exhibit a reduced kon rate by a factor of 5 and 2, respectively. Since KD values of 2′dAP binding to dGswC74U (60 µM) exceeds the KD of 2′dG binding to dGsw (250 nM), the determined koff for 2′dAP of 0.35 s−1 provides an upper limit for koff of 2′dG.
Fig. 4.
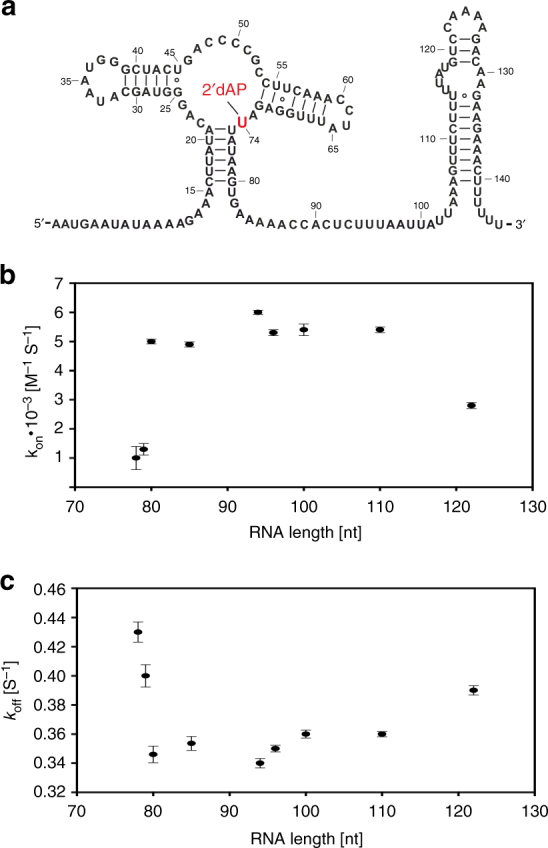
Ligand binding kinetics. a Secondary structure of dGswC74U highlighting the C to U mutation at position 74 in red to accommodate the fluorescence ligand analog 2-aminopurine-2′deoxyriboside (2′dAP). b Final kon and c koff rates of 2′dAP binding to dGswC74U derived from data shown in Supplementary Fig. 4 and Table 3 at varying transcript lengths. Errors correspond to the s.d. of the fit
Analysis of ligand binding by stopped-flow spectroscopy shows that ligand binding kinetics remains constant for stably formed aptamer domains regardless of transcript length. Due to decline in the ligand-bound equilibrium population between transcript length 90 and 110, the amount of structures accumulating within pathway 3 depends on cellular ligand concentration and corresponding kinetics of ligand association. Therefore, at saturating ligand concentration, the bound state (pathway 3) will be populated in a range of 70–100% by the time the polymerase has reached nucleotide 113. Equilibration can take place during transcription of nts 90–110, transcribing at rates of 0.5-4.5 s−1. From determined koff rates, we conclude that once bound, the ligand will not dissociate during the transcription interval for ligand binding.
Simulations of co-transcriptional folding
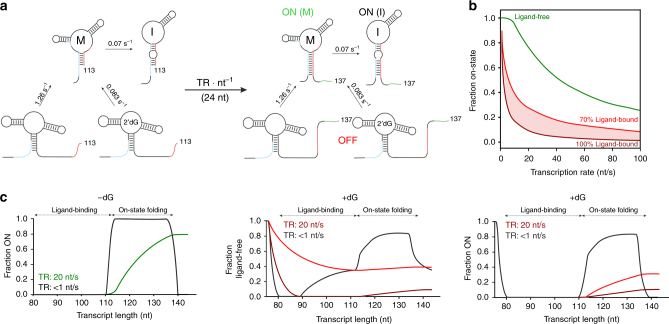
We determined all relevant conformational transition kinetics along and between pathways 1, 2, and 3 by real-time NMR and stopped-flow spectroscopy, allowing us to calculate the kinetics of the switch between different regulatory pathways (Fig. 5). We performed simulations of the conformational transition from PA–T to PAT between transcript lengths 113 and 137 at different transcription rates (0–100 nt s−1) (Supplementary Fig. 5) and derived the fraction of ON state after this transcription interval (Fig. 5a). Equilibration from the metastable PAT-H state to the PA–TH state can be initiated once nucleotide 139 emerges from the transcribing polymerase, one nucleotide prior to the regulatory signal. Therefore, we consider nucleotide 137 to represent the latest possible regulatory decision point. The fraction of ON state obtained from individual simulations at different transcription rates is shown in Fig. 5b for (i) 2′dG is not bound (in green) and (ii) 2′dG is bound by 70–100% (in red) to the PA–T conformation by the time nt 113 is synthesized. Figure 5c visualizes the effective ligand-induced kinetic delay of PT formation at a transcription rate of 20 nt s−1 that offsets equilibrium populations previously determined15. Kinetic traces between nucleotides 113 and 137 correspond to individual simulations derived from Supplementary Fig. 6. In the presence of ligand, the simulations further distinguish between OFF state (pathways 1 + 3) and ligand-bound state (pathways 3), where the OFF state includes ligand-free folded aptamer domains that also terminate transcription.
Fig. 5.
Simulations of co-transcriptional folding. a Schematic representation of interconverting transcriptional intermediates between transcript lengths 113 and 137 nt and corresponding refolding rates derived from real-time NMR experiments. b Fraction of ON state obtained at nucleotide 137 depending on the transcription rate. Individual simulations were performed for interconverting transcriptional intermediates between transcript lengths 113 and 137 nt based on interconversion rates derived from real-time NMR experiments. The following three instances were simulated: the ligand is not bound to the aptamer domain before nucleotide 113 is synthesized (ligand-free, green); ligand binding is completed by 70% (70% ligand-bound, light red) or 100% (100% ligand-bound, dark red). c Comparison of co-transcriptional folding at a transcription rate of 20 nt s−1 to equilibrium structures assuming the polymerase stalls at each nucleotide (<1 nt s−1). Equilibrium structures of transcriptional intermediates were determined previously (black trace)15. For a transcription rate of 20 nt s−1, simulations of co-transcriptional folding between transcript lengths 113 and 137 nt were fit into the corresponding graphs. The state adopted at nucleotide 137 is assumed to be maintained until the regulatory decision point. The ligand-free fraction between nucleotides 78 and 110 corresponds to a single-exponential decay resulting in either a 70% ligand-bound population at nucleotide 113 (~0.6 s−1) or a 100% ligand-bound population at nucleotide 90 (~2.3 s−1)
The simulations show that the riboswitch functions only at transcription rates of 10–50 nt s−1, a value that matches those typical for bacterial polymerases (Fig. 5b). Slow transcription rates <10 nt s−1 extend the time interval for ON state folding to a point, where ligand binding can no longer delay ON state folding sufficiently. At transcription rates exceeding 70 nt s−1, ON state folding in both absence and presence of ligand cannot compete with the rate of transcription. In this system of competing kinetic requirements, a maximum regulation efficiency of 40–50% is achieved only at transcription rates of 10–50 nt s−1. Comparison of static and kinetic experiments shows that the equilibration kinetics of metastable states neither lead to complete formation of the functional ON state from pathway 1 or preservation of the functional OFF state in pathway 3 during transcription.
In vitro transcription assays
We performed single-round in vitro transcription assays in the absence and presence of ligand using both, E. coli and B. subtilis DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RNAP) to (i) experimentally validate that the riboswitch functions only in a defined window of transcription rates and to (ii) assess whether the co-transcriptional folding pathway of the riboswitch is sensitive to the transcription properties of the polymerases from different organisms. We determined the dependence of transcription rates on temperature and NTP concentrations. We further determined the regulation efficiency by quantifying the amount of 235 nt fragments elongated past the terminator sequence.
For both polymerases, three pause sites (PS1) were determined in time-resolved transcription reactions. The first PS1 is encountered when the aptamer is fully transcribed (Fig. 6a, Supplementary Fig. 7). A decrease in temperature from 37 °C to 4 °C increases the t1/2 value of PS1 from 3 s to 50 s in the absence of ligand for E. coli RNAP. The second PS1 is located around nucleotide 116 at the 3′-end of segment T. This second PS1 pauses the transcription complex longer than the first PS1 (24 s at 37 °C). The third PS1 is located at the translation start site. This PS1 is located beyond the regulatory decision point and is, thus, not relevant for the co-transcriptional folding pathway of the riboswitch.
Fig. 6.
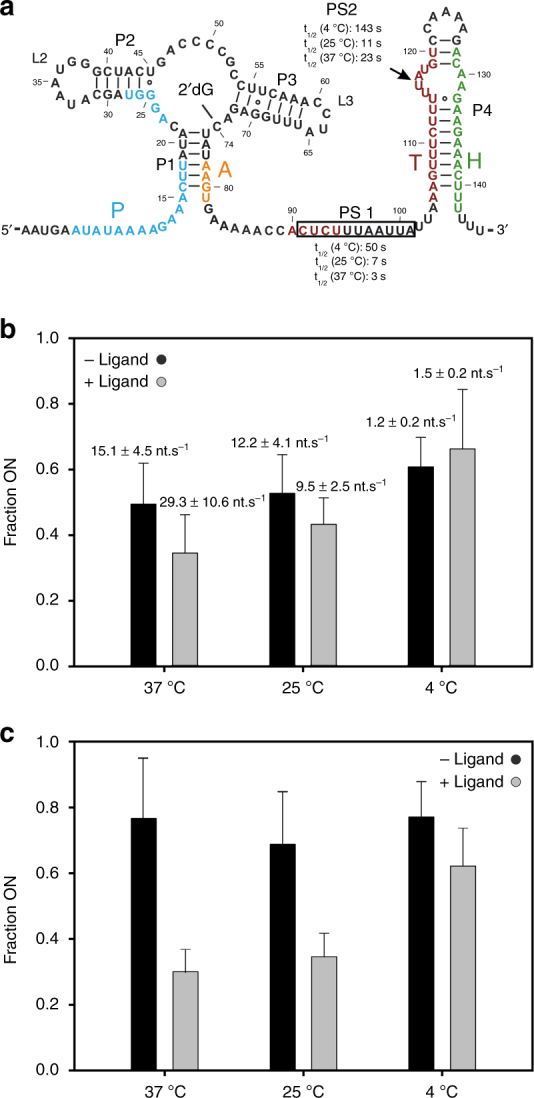
Fractions of ON state derived by in vitro transcriptions. a Secondary structure of dGsw illustrating determined pause sites including t1/2 values using E. coli polymerase (Supplementary Fig. 6 and Table 4 b, c) fractions of ON state from E. coli RNAP mediated b single-round and c multi-round in vitro transcriptions performed in the absence (black) and presence of ligand (gray) at 37 °C, 25 °C, and 4 °C with an NTP concentration of 0.05 mM (b) and 0.1 mM (c) (Supplementary Fig. 5, 6). Indicated transcription rates are correlated to the time point, at which half of the polymerases have transcribed the corresponding mRNA fragment
For the E. coli RNAP, the ligand-dependent ON state fraction is primarily affected by changes in temperature, while variations in the NTP concentration in the range of 0.05–2.3 mM do not affect the transcription rate sufficiently to cause changes in the co-transcriptional folding pathway (Supplementary Fig. 6). In the absence of ligand, the fractions of ON state represent 49–61% of all transcripts, and slightly increases with decreasing temperature (Fig. 6b). For the highest transcription rate (15.1 ± 4.5 nt s−1, 37 °C) (Supplementary Fig. 7) the fraction of ligand-independent ON state is 49 ± 12% and for the lowest transcription rate (1.2 ± 0.2 nt s−1, 4 °C) the fraction of ON state is 61 ± 9%. In line with riboswitch function, addition of ligand promotes accumulation of nascent transcripts within pathway 3 and decreases the fractions of ON state obtained to 35–43% for transcription reactions performed at 37 °C and 25 °C. For multi-round transcriptions, the effect of ligand addition on the fraction of ON state obtained is significantly more pronounced with 40–50% change in population ratio opposed to ~20% for single-round transcriptions (Fig. 5c). For transcription reactions performed at 4 °C, ligand addition does not cause significant changes in the population of ON state for both single-round and multi-round transcription.
For the B. subtilis RNAP, transcription rates could only be determined at 37 °C due to insufficient transcription efficiency at lower temperatures. Transcription rates for B. subtilis RNAP are higher compared to E. coli RNAP (34.7 ± 30.7 nt s−1) (Supplementary Fig. 7). In addition, the decrease in ON state population upon addition of ligand is significantly less pronounced. At an NTP concentration of 2.3 mM, ligand addition only induces a 5% shift in the fraction of ON state. Contrary to the behavior of E. coli polymerase, a decrease in the NTP concentration to 0.05 mM increases the ligand-induced shift in the fraction of ON state to 21%.
For E. coli polymerase, the overall regulation efficiency determined by transcription multi-round assays matches remarkably well with values predicted by our simulations of 40–50%, provided transcription reactions were performed close to the physiological temperature of E. coli. While an NTP-concentration range of 0.05–2.3 mM does not appear to affect transcription rates significantly to influence the co-transcriptional folding pathway of the riboswitch, a reduction in temperature to 4 °C leads to near-complete loss of riboswitch function. Determined transcription rates clearly show a negligibly small decrease in transcription speed from 37 °C to 25 °C, while transcription rates drop below the functional window of the riboswitch (<10 nt s−1) as determined by our simulation at 4 °C. In agreement with our simulations, slower transcription rates at 4 °C expand the time span available for PA–T to PAT(M) folding and lead to an increase in structures populating the ON state at the regulatory decision point in both absence and presence of ligand. In stark contrast, the B. subtilis polymerase requires a reduction in NTP concentration to induce transcription termination upon ligand addition. Due to the high percentage of full-length transcripts this effect is likely unrelated to ligand binding or ON state folding, but is linked to the inability of terminator formation due to the rapid elongation by the polymerase. The calculated transcription rates from the in vitro assays are not absolute values for single RNAPs, but instead are composite rates, as they indicate the point in time at which half of the RNAPs completed transcription of an RNA fragment of a specific length. This approximate rate can then be used in the simulations to examine the relationships of the different parameters in the regulation mechanism.
Discussion
To act as transcriptional regulatory elements, the sequence of riboswitches has to be optimized to fulfill a number of kinetics requirements. Our experimental approach delineates the competition between refolding rates of cis-regulatory RNA and processive transcript elongation. Within the regulatory decisive 2′dG concentration range of 0.1–100 µM for dGsw26, ligand association rates for purine aptamer domains of ~104–105 M−1 s−1 27,28 can effectively direct ligand-binding to either compete with or lag behind bacterial polymerases synthesizing the relevant ligand-binding sequence at rates of 0.5–4.5 s−1. Remarkably, PS1 induces transcriptional stalling at the latest possible transcript length with highest ligand binding affinity according to previous results29. To determine shifts in population ratios as transcription proceeds further, we present a ligation-based approach that provides access to reversible trapping of metastable states that form within the activation (pathway 1) and repression pathway (pathway 3) of ON function (pathway 2). In the biological context of co-transcriptional folding, single nucleotides are sequentially released to an ensemble of RNA intermediates differing in length that are transcribed at locally varying transcription rates. Real-time monitoring of such folding is experimentally challenging and cannot be accomplished by established methods. In the approach applied here, folding is monitored by immediately releasing a part of the riboswitch expression platform to interact with the aptamer domain. Despite these experimental limitations, we have selected a representative transcription intermediate that most accurately reflects refolding rates of the metastable state on average to obtain high-quality quantitative data. We linked kinetics derived from light-induced release of the stable ON state to unbiased mapping of conformational space15 to assess the kinetics of ligand-dependent conformational switch. We further experimentally validated the impact of transcription rates and polymerase dependent transcription properties on the regulation efficiency of the riboswitch using E. coli and B. subtilis RNAP.
Our results demonstrate the requirement for a strict synchronization of transcription intervals of metastable states, corresponding transcription rates, and refolding rates, where transcription elongation must not only be matched to refolding and ligand binding kinetics but also to folding delays induced by thermodynamic stabilizations to preserve metastable states within distinct sequence intervals. A significant offset in temperature from physiological conditions leads to quantitative folding to the ON state from both metastable ligand-bound and ligand-free aptamer domains. Sequence-specific variations in transcription rates impact both ON state folding from pathways 1 and 3 equally. Therefore, it is critical that pausing within the expression platform is adapted to the sequence-specific transcription speed of the native polymerase. In a previous study we could already show that the detailed investigation of transcriptional riboswitches requires the native RNA polymerase30. Here, we further substantiate this proposal by revealing the difference in co-transcriptional riboswitch folding transcribed by two non-native polymerases. Furthermore, biologically demanding experiments with M. florum polymerase would be required to compare these results to native 2′dG riboswitch folding. General fluctuations in transcription rates resulting from changes in cellular conditions31 may be self-regulated by the negative feedback loop of the riboswitch itself. The kinetic and simulation framework developed here provides an important contribution to the conceptual basis to understand transcriptional riboswitches.
Methods
Sample preparation
dGsw85 and mutated dGswC74U constructs with varying length for stopped-flow spectroscopy were prepared by in vitro transcription from PCR products by adjusting the reverse primers accordingly as reported previously32. For dGswC74U constructs, two artificial G’s were incorporated at the 5′-end in the forward primers to enable rapid RNA purification by buffer exchange. dGsw85 was transcribed with a 5′-hammerhead ribozyme, exchanged into water, and directly used for ligation reactions.
Photocaged dGsw86–121 was prepared via solid phase synthesis in a 17 µmol scale. Ultramild phosphoramidites, chemical phosphorylation reagent I, and (S)-NPE-U phosphoramidite (Supplementary Fig. 2) were used and a postsynthetic DEA wash performed. The use of NH3:EtOH (3:1) for deprotection primarily generates a byproduct with a mass 53 Da greater than the desired product (Supplementary Table 1). The dGsw86–121 fragment could be isolated using 3 mL t-BuNH2:water (1:3) for 6 hours at 60 °C. The mixture was separated in 10 reaction tubes and the solvent evaporated. Each tube was treated as follows: the 2′-deprotection was performed using 6.5 mL of a mixture of NMP:Et3N:Et3N·3 HF (3:1.5:2) for 3 hours at 60 °C. After addition of 30 mL n-BuOH the mixture was stored at −80 °C for 2 hours and then centrifuged at −8 °C for 1 hour. The supernatant was decanted and the residue purified via anion exchange HPLC (Amersham Bioscience with an UV-900 detector and P-900 pumps) using a Tricorn SOURCE 15Q AEX 10/150 column (gradient: 0–100% 0.35 M LiClO4 in water in 17 column volumes, flow: 4 mL min−1). The collected oligoribonucleotide was desalted using a Tricorn SOURCE 15 RPC 10/150 column (gradient: 5–40% MeCN in 0.1 M TEAA buffer pH 7 in 9 column volumes, flow: 4 mL min−1). The identity of the oligoribonucleotide was confirmed by ESI-MS: mass calculated: 11784.5 Da, found: 11785.7 Da.
Photocaged dGsw121 was prepared by enzymatic splinted ligation using T4 RNA ligase 2. Fragments dGsw85 (15N-G/U) and photocaged dGsw86–121 were preannealed to a 31 nt splint (splint:31AATAATTAAAGAGTGGTTTTTCACTTATAGT) prior to ligation at 25 °C for 15 min. Ligation reactions were performed with 12.5 µM dGsw85, 6.25 µM caged dGsw86–121, 10 µM splint31, 48 µg mL−1 T4 RNA ligase 2 (homemade), 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM ATP, 25 mM DTT in 50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4. dGsw85 was applied in 2-fold excess to optimize the turnover for photocaged dGsw86–121 (80%). Ligation reactions were incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours followed by overnight incubation at 25 °C, followed by incubation with TURBO DNAse (0.02 U µL−1) (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 8 hours. Ligation reactions were directly applied to HPLC using a Kromasil RP18 10 × 250 column without further concentration and eluted at room temperature (gradient: 0–40% MeCN in 0.1 M TEAA, pH 6.0). Purified photocaged dGsw121 was lyophilized and exchanged into NMR buffer (50 mM KCl, 25 mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4, pH 6.2). Final yield of photocaged dGsw86–121 was 0.6 µmol (54 %).
NMR-spectroscopy
Time-resolved NMR experiments were performed as reported previously17,18,33 in a pseudo-2D experiment using the jump return echo water suppression scheme34. Laser irradiation within the NMR tube was triggered via a TLL connection to a laser set up (Paladin Advanced 355-8000). Kinetics of ligand-free samples were recorded after 500 ms and kinetics of ligand-bound RNAs after 1 s of laser irradiation. The signal intensity was maximized by Ernst angle excitation35. Kinetics traces of ligand-free samples were averaged over 10 individual experiments and of ligand-bound samples over two individual experiments on 100 µM caged dGsw121 samples. 1H,15N-BEST-TROSY experiments were recorded with modifications according to Brutscher et al36,37. NMR experiments were performed on a Bruker 800 MHz spectrometer equipped with a 5-mm z-axis TCI-HCN cryogenic probe. For processing of data, Topspin 3.5 (Bruker Biospin) was used.
Stopped-flow spectroscopy
Stopped-flow measurements were performed on a π*-180 CDF-spectrometer (Applied Photophysics). Folding was monitored by rapid mixing of dGswC74U (2 µM) with 2-aminopurine 2′-deoxyriboside (2 µM–512 µM) in a 1:1 volume ratio at 25 °C. Both ligand and RNA were provided in NMR buffer with a Mg2+ concentration of 3 mM. 2′dAP was excited at 304.5 nm using 2 mm slit widths and fluorescence was monitored at >340 nm. Kinetic traces were averaged over 10–15 single measurements. Fluorescence decays were fitted with single and bi-exponential decays with three and five parameters, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 4). Association (kon) and dissociation (koff) constants were determined from individual apparent rate constants according to equation (1) (Supplementary Table 3):
| 1 |
Simulations of co-transcriptional folding
Simulations of co-transcriptional folding were performed by kinetic Markov simulations. Simulations were performed as described previously15, starting from the aptamer domain fold at transcript length of 113 nt, followed by simultaneous elongation to a transcript length of 137 nt at transcription rates of 10–100 nt s−1 and folding to the antiterminator conformations PAT(M) and PAT(I) with rate constants determined by real-time NMR.
Time-resolved transcriptions
The DNA template used for E. coli and B. subtilis RNAP mediated transcription was composed of the lambdaPR promoter followed by the dGsw-coding sequence (GCAAATCGCGCTGTTAGCGGGCccttgactattttacctctggcggtgataatggttgcATGAATATAAAAGAAACTTATACAGGGTAGCATAATGGGCTACTGACCCCGCCTTCAAACCTATTTGGAGACTATAAGTGAAAAACCACTCTTTAATTATTAAAGTTTCTTTTTATGTCCAAAAGACAAGAAGAAACTTTTTTATTTAGTTGAATTTATAATAAGAGAAAAAGAAAGGATATTATATGGCAAAAATAAAAAACCAATATTACAACGAGTCTGTTTCGCCAATTG). The time-resolved transcriptions were performed as described previously30 at 37 °C, 25 °C, and 4 °C with NTP concentrations of 0.05 mM, 0.1 mM, 1 mM, and 2.3 mM. Transcription rates were determined as described previously38 and PS1 were analyzed as described by Landick 199639.
Data availability
The data that support the findings within study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by DFG (CRC 902 and GRK 1986 “CLiC”), and Fonds der Chemischen Industrie (C.H.). H.S. and A.H. are members of the DFG-funded cluster of excellence: dynamics of macromolecular complexes (EXC 115). BMRZ is supported by the state of Hesse.
Author contributions
C.H., D.-P.K., F.S., and R.A.M. performed experiments. D.-P.K. conducted the chemical synthesis of the photocaged RNA. F.S., and R.A.M. performed transcription assays. All other experiments were conducted by C.H. The contributions by C.H. and D.-P.K. were both essential for the work, C.H. and D.-P.K. should be regarded as joint first authors. All authors contributed to the design of the experiments, analysis of data, discussion, and writing of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Christina Helmling, Dean-Paulos Klötzner, Alexander Heckel.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41467-018-03375-w.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Alexander Heckel, Email: heckel@uni-frankfurt.de.
Harald Schwalbe, Email: schwalbe@nmr.uni-frankfurt.de.
References
- 1.Mironov AS, et al. Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in bacteria. Cell. 2002;111:747–756. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Winkler WC, Cohen-Chalamish S, Breaker RR. An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:15908–15913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212628899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lemay JF, et al. Comparative study between transcriptionally- and translationally-acting adenine riboswitches reveals key differences in riboswitch regulatory mechanisms. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1001278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith AM, Fuchs RT, Grundy FJ, Henkin TM. The SAM-responsive S(MK) box is a reversible riboswitch. Mol. Microbiol. 2010;78:1393–1402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Suddala KC, et al. Single transcriptional and translational preQ1 riboswitches adopt similar pre-folded ensembles that follow distinct folding pathways into the same ligand-bound structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:10462–10475. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Haller A, Soulière MF, Micura R. The dynamic nature of RNA as key to understanding riboswitch mechanisms. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011;44:1339–1348. doi: 10.1021/ar200035g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Reining A, et al. Three-state mechanism couples ligand and temperature sensing in riboswitches. Nature. 2013;499:355–359. doi: 10.1038/nature12378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.d’Aubenton Carafa Y, Brody E, Thermes C. Prediction of rho-independent Escherichia coli transcription terminators. A statistical analysis of their RNA stem-loop structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;216:835–858. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(99)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rosenberg M, Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wickiser JK, Winkler WC, Breaker RR, Crothers DM. The speed of RNA transcription and metabolite binding kinetics operate an FMN riboswitch. Mol. Cell. 2005;18:49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lutz B, Faber M, Verma A, Klumpp S, Schug A. Differences between cotranscriptional and free riboswitch folding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:2687–2696. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Frieda KL, Block SM. Direct observation of cotranscriptional folding in an adenine riboswitch. Science. 2012;338:397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.1225722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Watters KE, Strobel EJ, Yu AM, Lis JT, Lucks JB. Cotranscriptional folding of a riboswitch at nucleotide resolution. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016;23:1124–1131. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rieder R, Lang K, Graber D, Micura R. Ligand-induced folding of the adenosine deaminase A-Riboswitch and implications on riboswitch translational control. ChemBioChem. 2007;8:896–902. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Helmling C, et al. NMR structural profiling of transcriptional intermediates reveals riboswitch regulation by metastable RNA conformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:2647–2656. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b10429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wenter P, Fürtig B, Hainard A, Schwalbe H, Pitsch S. Kinetics of photoinduced RNA refolding by real-time NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:2600–2603. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fürtig B, et al. Time-resolved NMR studies of RNA folding. Biopolymers. 2007;86:360–383. doi: 10.1002/bip.20761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kühn T, Schwalbe* H. Monitoring the kinetics of ion-dependent protein folding by time-resolved NMR spectroscopy at atomic resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:6169–6174. doi: 10.1021/ja994212b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wacker A, et al. Structure and dynamics of the deoxyguanosine-sensing riboswitch studied by NMR-spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:6802–6812. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Adelman K, et al. Single molecule analysis of RNA polymerase elongation reveals uniform kinetic behavior. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:13538–13543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212358999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tolić-Nørrelykke SF, Engh AM, Landick R, Gelles J. Diversity in the rates of transcript elongation by single RNA polymerase molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:3292–3299. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310290200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bremer H, Yuan D. RNA chain growth-rate in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1968;38:163–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90404-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Manor H, Goodman D, Stent GS. RNA chain growth rates in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1969;39:1–27. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mandal M, Breaker RR. Adenine riboswitches and gene activation by disruption of a transcription terminator. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:29–35. doi: 10.1038/nsmb710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Roth A, et al. A riboswitch selective for the queuosine precursor preQ1 contains an unusually small aptamer domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007;14:308–317. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim JN, Roth A, Breaker RR. Guanine riboswitch variants from Mesoplasma florum selectively recognize 2’-deoxyguanosine. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:16092–16097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705884104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wickiser JK, Cheah MT, Breaker RR, Crothers DM. The kinetics of ligand binding by an adenine-sensing riboswitch. Biochemistry. 2005;44:13404–13414. doi: 10.1021/bi051008u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gilbert SD, Stoddard CD, Wise SJ, Batey RT. Thermodynamic and kinetic characterization of ligand binding to the purine riboswitch aptamer domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;359:754–768. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Helmling C, et al. NMR structural profiling of transcriptional intermediates reveals riboswitch regulation by metastable RNA conformations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:2647–2656. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b10429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Steinert H, et al. Pausing guides RNA folding to populate transiently stable RNA structures for riboswitch-based transcription regulation. eLife. 2017;6:e21297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vogel U, Jensen KF. The RNA chain elongation rate in Escherichia coli depends on the growth rate. J. Bacteriol. 1994;176:2807–2813. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.2807-2813.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Helmling C, et al. Rapid NMR screening of RNA secondary structure and binding. J. Biomol. NMR. 2015;63:67–76. doi: 10.1007/s10858-015-9967-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wenter P, Fürtig B, Hainard A, Schwalbe H, Pitsch S. Kinetics of photoinduced RNA refolding by real-time NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:2600–2603. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sklenář V, Bax A. Spin-Echo water suppression for the generation of pure-phase two-dimensional NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 1987;74:469–479. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ernst, R. R., Bodenhausen, G. & Wokaun, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One And Two Dimensions. (1987).
- 36.Favier A, Brutscher B. Recovering lost magnetization: polarization enhancement in biomolecular NMR. J. Biomol. NMR. 2011;49:9–15. doi: 10.1007/s10858-010-9461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lescop E, Kern T, Brutscher B. Guidelines for the use of band-selective radiofrequency pulses in hetero-nuclear NMR: example of longitudinal-relaxation-enhanced BEST-type 1H-15N correlation experiments. J. Magn. Reson. 2010;203:190–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2009.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ederth J, Mooney RA, Isaksson LA, Landick R. Functional interplay between the jaw domain of bacterial RNA polymerase and allele-specific residues in the product RNA-binding pocket. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;356:1163–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Landick R, Wang D, Chan CL. Quantitative analysis of transcriptional pausing by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: his leader pause site as paradigm. Methods Enzymol. 1996;274:334–353. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(96)74029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings within study are available from the corresponding author upon request.