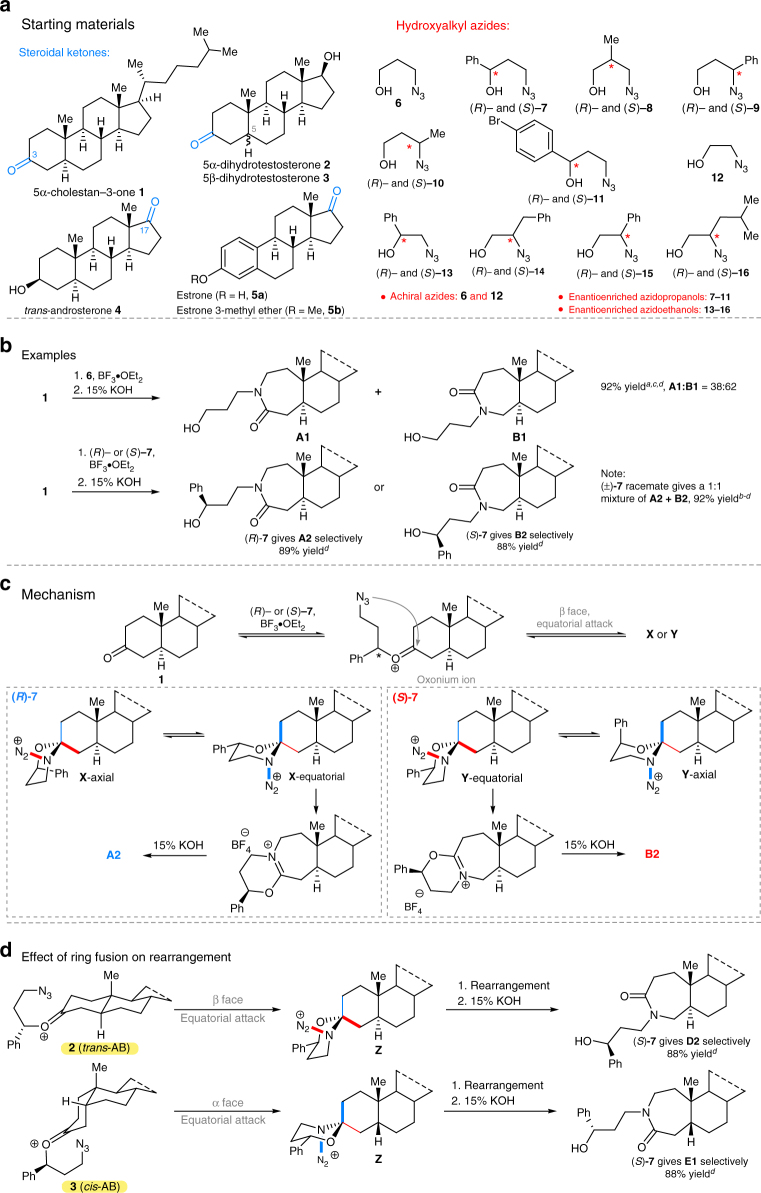
Fig. 2.
Regioselective ring expansions of 3-oxosteroids. a Steroids and hydroxyalkyl azides used in this study. The blue ketones indicate modification sites. b Ring expansions obtained by treating 1 with 3-azidopropanol 6, 3-azido-1-phenylpropanol (R)-7 and (S)-7. c Mechanistic rationale for ring expansion chemistry differentiating between C-2 (blue bond) and C-4 (red bond) migration; key antiperiplanar relationship between the migrating group and the N2+ leaving group is indicated by bold bonds. d Dependence of migration outcome on C-5 stereochemistry. aInseparable mixture by normal phase chromatography. bSeparable mixture by normal phase chromatography, but for this control experiment the isomers were not separated. cRatio determined by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). dIsolated yield after chromatography on silica. See Supplementary Methods for full synthetic details. A and B series are 5α-cholestan-3-one derivatives; D2 is a 5α-dihydrotestosterone derivative; E1 is a 5β-dihydrotestosterone derivative; X and Y are proposed spirocyclic intermediates (including both chair conformers as designated); 15% KOH, 15% aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide; *, signifies site of stereochemistry