Figure 2.
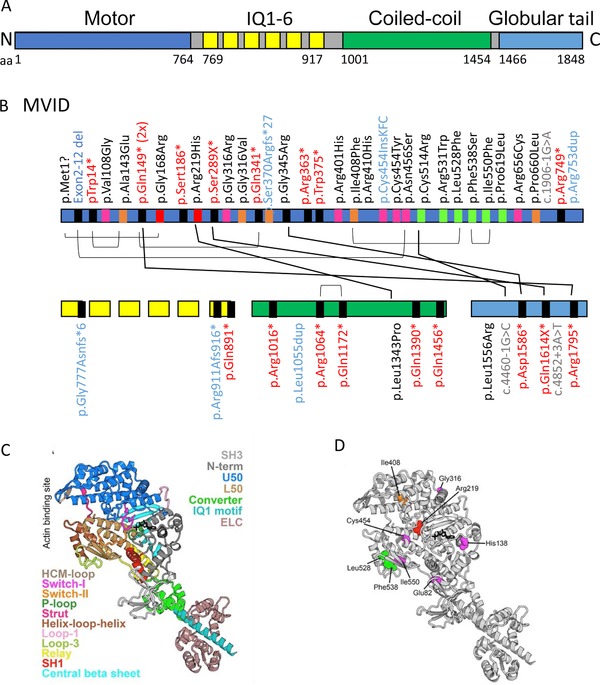
Schematic representation of the myosin Vb protein. A: A schematic overview of the myosin Vb protein and its functional domains. Protein data are deduced from Genbank RefSeq‐file accession number NG_012925.1 for the human MYO5B gene. Nucleotide numbering reflects cDNA numbering with +1 corresponding to the A of the ATG translation initiation codon in the reference sequence, according to the journal guidelines (www.hgvs.org/mutnomen). The initiation codon is 1. B: Overviews of the MVID‐associated MYO5B mutations in the different domains of the myosin Vb protein. IQ1‐6 refers to the six calmodulin‐binding IQ domains that conform to the consensus sequence [I,L,V]QxxxRGxxx[R,K]. Mutations indicated in black, red, blue, and gray letter color represent missense, frameshift/nonsense, deletions/insertions, and splicing mutations, respectively. The differently colored blocks associated with each mutation in the protein domains represent the predicted consequences for the protein (black: premature termination, magenta: mutations in regions important for the allosteric rearrangements of the myosin motor head during the kinetic cycle, orange: mutations that may lead to protein misfolding, red: mutations in the ATP‐binding site, green: mutations in regions that are important for actin interactions). Black lines between individual mutations indicate their combined presence in a single patient. C: Model of the myosin Vb motor domain. A. Homology model of myosin Vb based on myosin Va post‐rigor structure with ATP nucleotide bound (PDB ID: 1W7J) is shown. The motor domain contains four subdomains (the N‐terminal: gray, including the SH3: light gray, the U50: marine blue, the L50: sand, and the converter: green). Conformational changes in the motor domain are amplified by the lever arm (converter, green; IQ motif 1, pale cyan helix associated with a calmodulin (light pink); the 5 other IQ motifs of the lever arm are not shown). These conformational changes are coordinated within the motor by elements of the transducer (loop 1: light purple, central beta sheet: cyan) as well as the connectors (Relay: yellow, SH1 helix: red, Strut: hot pink), which are linkers between subdomains. The nucleotide‐binding elements (P‐loop: pale green, Switch I: magenta, and switch II: orange) surrounding the nucleotide (represented in black sticks) and the actin‐binding elements (helix‐loop‐helix: brown, HCM loop: wheat) are also depicted. D: The MVID‐associated missense mutations found in the motor domain of myosin Vb are depicted with the following color code: (green: mutations in regions that are important for actin interactions, red: mutations in the ATP‐binding site, Magenta: mutations in regions of importance for allosteric rearrangements of the myosin head during the motor cycle, orange: mutations that may lead to protein misfolding)
