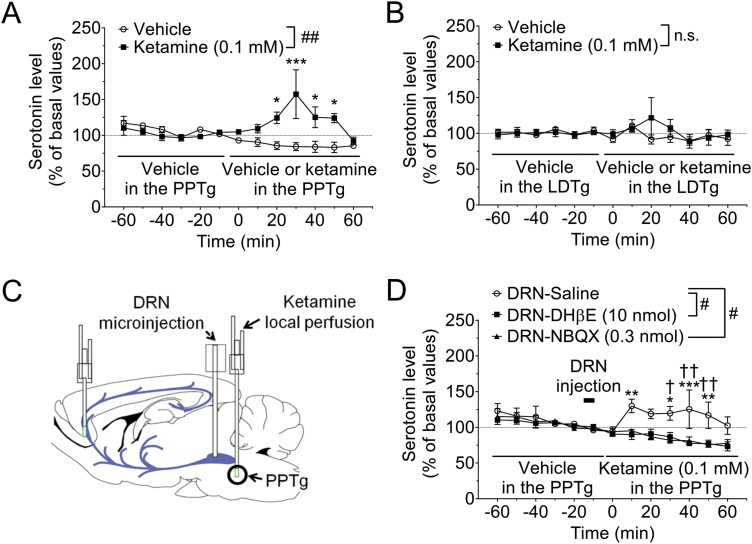
Figure 2.
α4β2 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α4β2 nAChR) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) mediates prefrontal serotonin release induced by local perfusion of PPTg with ketamine. (A, B) Effects of local perfusion with ketamine of pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPTg) (A) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDTg) (B) on serotonin release in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Extracellular serotonin levels in the mPFC were continuously measured for 120 min by in vivo microdialysis before and after local perfusion with ketamine. The horizontal lines indicate the unilateral perfusion with vehicle or ketamine (0.1 mM). ##P<.01 main effect in 2-way ANOVA, ***P<.001, *P<.05 vs vehicle group by Bonferroni posthoc test. n.s., not significant, n=3–6. Basal values for serotonin concentrations were 0.64±0.17 nM (PPTg-vehicle), 0.50±0.05 nM (PPTg-ketamine), 0.55±0.05 nM (LDTg-vehicle), and 0.49±0.05 nM (LDTg-ketamine). (C) Schematic presentation of the experimental procedure. (D) Extracellular serotonin levels in the mPFC were continuously measured for 120 min before and after local perfusion of PPTg with ketamine by in vivo microdialysis. Saline, DHβE (10 nmol), an α4β2 nAChR antagonist, or NBQX (0.3 nmol), an AMPAR antagonist, was microinjected into the DRN from −15 to −10 min (bar). Then, ketamine (0.1 mM) was unilaterally perfused in the PPTg at 0 min (horizontal lines). #P<.05 main effect in 2-way ANOVA, ***P<.001, **P<.01, *P<.05 vs DRN-DHβE group by Bonferroni posthoc test. ††P<.01, †P<.05 vs DRN-NBQX group by Bonferroni posthoc test, n=4–6. Basal values for serotonin concentrations were 0.45±0.09 nM (DRN-saline), 0.44±0.06 nM (DRN-DHβE), and 0.48±0.09 nM (DRN-NBQX).